Overview on the Discovery and Development of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Should the Focus Be on Synthesis or Degradation of PGE2?
- PMID: 33568930
- PMCID: PMC7868279
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S278514
Overview on the Discovery and Development of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Should the Focus Be on Synthesis or Degradation of PGE2?
Abstract
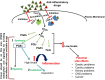
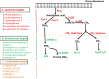
Inflammation is a protective response that develops against tissue injury and infection. Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, is the key player in the pathogenesis of many inflammatory disorders including cancer. The cytokine storm, an inflammatory response flaring out of control, is mostly responsible for the mortality in COVID-19 patients. Anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit cyclooxygenases (COX), which are involved in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins that promote inflammation. The conventional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are associated with gastric and renal side-effects, as they inhibit both the constitutive COX-1 and the inducible COX-2. The majority of selective COX-2 inhibitors (COXIBs) are without gastric side-effects but are associated with cardiac side-effects on long-term use. The search for anti-inflammatory drugs without side-effects, therefore, has become a dream and ongoing effort of the Pharma companies. As PGE2 is the key mediator of inflammatory disorders, coming up with a strategy to reduce the levels of PGE2 alone without affecting other metabolites may form a better choice for the development of next generation anti-inflammatory drugs. In this direction the options being explored are on synthesis of PGE2-mPGES-1; PGE2 degradation through a specific PG dehydrogenase, 15-PGDH, and by blocking its activity mediated through a specific PGE receptor, EP4. As leukotrienes formed via the 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) pathway also play an important role in the mediation of inflammation, efforts are also being made to target both COX and LOX pathways. This review focuses on addressing the following three points: 1) How NSAIDs and COXIBs are associated with gastric, renal and cardiac side-effects; 2) Should the focus be on the targets upstream or downstream of PGE2; and 3) the status of alternative targets being explored for the discovery and development of anti-inflammatory drugs without side-effects.
Keywords: 15-PGDH; 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase; 5-LOX; 5-lipoxygenase; COX; COXIBs; NSAIDs; cyclooxygenase; inflammation; mPGES-1; microsomal PGE synthase-1.
© 2021 Mahesh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

