Creatinine Trends to Detect Ibuprofen-Related Maturational Adverse Drug Events in Neonatal Life: A Simulation Study for the ELBW Newborn
- PMID: 33569003
- PMCID: PMC7868337
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.610294
Creatinine Trends to Detect Ibuprofen-Related Maturational Adverse Drug Events in Neonatal Life: A Simulation Study for the ELBW Newborn
Abstract
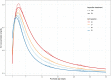
Background: Recognizing a change in serum creatinine concentrations is useful to detect a renal adverse drug reaction signal. Assessing and characterizing the nephrotoxic side-effects of drugs in extremely low birth weight (ELBW, ≤1000 g) neonates remain challenging due to the high variability in creatinine in this population. This study aims to investigate and quantify the impact of ibuprofen treatment on kidney function, reflected by serum creatinine. Method: A recently developed dynamical model for serum creatinine was used to simulate creatinine profiles for typical, reference ELBW neonates with varying gestational and postnatal ages whilst being exposed to ibuprofen treatment. Results: The increase of serum creatinine concentrations due to ibuprofen treatment is most apparent during the first week of life. The difference in serum creatinine values between ibuprofen-exposed vs. non-exposed neonates decreases with increasing postnatal age, independent of gestational age. Conclusion: The difference in serum creatinine concentrations between ibuprofen-exposed vs. non-exposed neonates decreases with postnatal age, indicating an increased clearing capacity and resulting in a weak ibuprofen-related adverse drug reaction signal beyond early neonatal life.
Keywords: ELBW neonates; creatinine clearance; ibuprofen; nephrotoxicity; serum creatinine.
Copyright © 2021 van Donge, Allegaert, Pfister, Smits and van den Anker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Allegaert K., Smits A., van Donge T., van den Anker J., Sarafidis K., Levtchenko E., et al. (2020). Renal precision medicine in neonates and acute kidney injury: how to convert a cloud of creatinine observations to support clinical decisions. Front. Pediatr. 8, 366 10.3389/fped.2020.00366 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

