The serine hydroxymethyltransferase-2 (SHMT2) initiates lymphoma development through epigenetic tumor suppressor silencing
- PMID: 33569544
- PMCID: PMC7872152
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-020-0080-0
The serine hydroxymethyltransferase-2 (SHMT2) initiates lymphoma development through epigenetic tumor suppressor silencing
Abstract
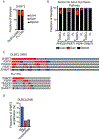
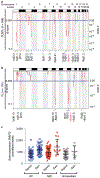
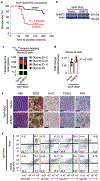
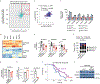
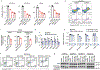
Cancer cells adapt their metabolic activities to support growth and proliferation. However, increased activity of metabolic enzymes is not usually considered an initiating event in the malignant process. Here, we investigate the possible role of the enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase-2 (SHMT2) in lymphoma initiation. SHMT2 localizes to the most frequent region of copy number gains at chromosome 12q14.1 in lymphoma. Elevated expression of SHMT2 cooperates with BCL2 in lymphoma development; loss or inhibition of SHMT2 impairs lymphoma cell survival. SHMT2 catalyzes the conversion of serine to glycine and produces an activated one-carbon unit that can be used to support S-adenosyl methionine synthesis. SHMT2 induces changes in DNA and histone methylation patterns leading to promoter silencing of previously uncharacterized mutational genes, such as SASH1 and PTPRM. Together, our findings reveal that amplification of SHMT2 in cooperation with BCL2 is sufficient in the initiation of lymphomagenesis through epigenetic tumor suppressor silencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests A.D. has received personal consultancy fees from Roche, Corvus Pharmaceuticals, Physicians’ Education Resource, Seattle Genetics, Takeda, EUSA Pharma and AbbVie, and research grants from Roche. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

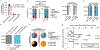


References
-
- Basso K & Dalla-Favera R Germinal centres and B cell lymphomagenesis. Nat. Rev. Immunol 15, 172–184 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Huet S, Sujobert P & Salles G From genetics to the clinic: a translational perspective on follicular lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 18, 224–239 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Haluska FG, Finver S, Tsujimoto Y & Croce CM The t(8; 14) chromosomal translocation occurring in B-cell malignancies results from mistakes in V–D–J joining. Nature. 324, 158–161 (1986). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

