Chemical Properties Determine Solubility and Stability in βγ-Crystallins of the Eye Lens
- PMID: 33569867
- PMCID: PMC8052307
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202000739
Chemical Properties Determine Solubility and Stability in βγ-Crystallins of the Eye Lens
Abstract
βγ-Crystallins are the primary structural and refractive proteins found in the vertebrate eye lens. Because crystallins are not replaced after early eye development, their solubility and stability must be maintained for a lifetime, which is even more remarkable given the high protein concentration in the lens. Aggregation of crystallins caused by mutations or post-translational modifications can reduce crystallin protein stability and alter intermolecular interactions. Common post-translational modifications that can cause age-related cataracts include deamidation, oxidation, and tryptophan derivatization. Metal ion binding can also trigger reduced crystallin solubility through a variety of mechanisms. Interprotein interactions are critical to maintaining lens transparency: crystallins can undergo domain swapping, disulfide bonding, and liquid-liquid phase separation, all of which can cause opacity depending on the context. Important experimental techniques for assessing crystallin conformation in the absence of a high-resolution structure include dye-binding assays, circular dichroism, fluorescence, light scattering, and transition metal FRET.
Keywords: beta-gamma-crystallin; cataracts; long-lived proteins; protein aggregation; protein solubility.
© 2021 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors are not aware of any affiliations, memberships, funding, or financial holdings that might be perceived as affecting the objectivity of this review.
Figures
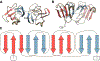
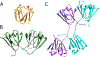


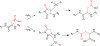




References
-
- Patel S, Marshall J, Fitzke FWI 1995. J. Cataract Refractive Surg 11, 100–105. - PubMed
-
- Jagger W 1992. Vis. Res 32, 1271–1284. - PubMed
-
- Kröger RHH, Campbell MCW, Munger R, Fernald RD 1994. Vis. Res 34, 1815–1822. - PubMed
-
- Garner LF, Smith GT, Yao S, Augusteyn RC 2001. Vis. Res 41, 973–979. - PubMed
-
- Wistow GJ, Piatigorsky J 1988. Annu. Rev. Biochem 57, 479–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

