Caffeinated Coffee Consumption and Health Outcomes in the US Population: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis and Estimation of Disease Cases and Deaths Avoided
- PMID: 33570108
- PMCID: PMC8321867
- DOI: 10.1093/advances/nmaa177
Caffeinated Coffee Consumption and Health Outcomes in the US Population: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis and Estimation of Disease Cases and Deaths Avoided
Abstract
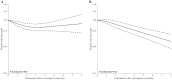
To explore the role of coffee on health outcomes in the United States, where coffee consumption is common, we conducted a meta-analysis of prospective studies investigating the magnitude (any compared with no consumption) and the dose-response shape (cups per day) of the associations between caffeinated coffee consumption and incidence/mortality of cardiovascular disease (CVD), as well as incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2D), hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), endometrial cancer, melanoma, and nonmelanoma skin cancer. We selected the desirable health outcomes that have been shown to be positively associated with coffee consumption. Studies were identified by searching PubMed/Embase databases up to September 2019. Inclusion criteria included prospective studies that investigated the relation of ≥3 categories of caffeinated coffee consumption and the outcomes of interest. Twenty-six studies (42 distinct cohorts), with 93,706 cases/deaths and 3,713,932 participants, met the inclusion criteria. In any coffee consumers, there was a significant inverse association with the risk of CVD (RR = 0.90; 95% CI: 0.84, 0.96), T2D (RR = 0.90; 95% CI: 0.85, 0.96), endometrial cancer (RR = 0.85; 95% CI: 0.78, 0.92), melanoma (RR = 0.89; 95% CI: 0.80, 0.99), and nonmelanoma skin cancer (RR = 0.92; 95% CI: 0.89, 0.95). Coffee consumption was also inversely associated with HCC (RR = 0.93; 95% CI: 0.80, 1.08), without reaching statistical significance. The dose-response relation was nonlinear uniquely for CVD (P-nonlinearity = 0.01). In particular, the largest risk reduction was observed for 3-4 cups/d (∼120 mL/cup) and no reduction thereafter. For other outcomes, the risk decreased linearly over the whole coffee consumption range. Current patterns of consumption in the United States would account for a fraction of avoided cases/deaths ranging from 6% to 12% according to the outcome considered. This study confirms the beneficial health effects of caffeinated coffee consumption in the US population on the health outcomes considered, and quantifies their possible magnitude.
Keywords: US population; attributable fraction; caffeinated coffee consumption; dose–response shape; health outcomes.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society for Nutrition.
Figures



References
-
- Jeszka-Skowron M, Krawczyk M, Zgola-Grzeskowiak A. Determination of antioxidant activity, rutin, quercetin, phenolic acids and trace elements in tea infusions: influence of citric acid addition on extraction of metals. J Food Compos Anal. 2015;40:70–7.
-
- Noordzij M, Uiterwaal CS, Arends LR, Kok FJ, Grobbee DE, Geleijnse JM. Blood pressure response to chronic intake of coffee and caffeine: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Hypertens. 2005;23:921–8. - PubMed
-
- Jee SH, He J, Appel LJ, Whelton PK, Suh I, Klag MJ. Coffee consumption and serum lipids: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Am J Epidemiol. 2001;153:353–62. - PubMed
-
- Rebello SA, van Dam RM. Coffee consumption and cardiovascular health: getting to the heart of the matter. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2013;15:403. - PubMed
-
- van Dam RM, Feskens EJ. Coffee consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 2002;360:1477–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

