Subcortical volumes across the lifespan: Data from 18,605 healthy individuals aged 3-90 years
- PMID: 33570244
- PMCID: PMC8675429
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.25320
Subcortical volumes across the lifespan: Data from 18,605 healthy individuals aged 3-90 years
Abstract
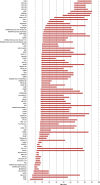
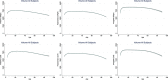
Age has a major effect on brain volume. However, the normative studies available are constrained by small sample sizes, restricted age coverage and significant methodological variability. These limitations introduce inconsistencies and may obscure or distort the lifespan trajectories of brain morphometry. In response, we capitalized on the resources of the Enhancing Neuroimaging Genetics through Meta-Analysis (ENIGMA) Consortium to examine age-related trajectories inferred from cross-sectional measures of the ventricles, the basal ganglia (caudate, putamen, pallidum, and nucleus accumbens), the thalamus, hippocampus and amygdala using magnetic resonance imaging data obtained from 18,605 individuals aged 3-90 years. All subcortical structure volumes were at their maximum value early in life. The volume of the basal ganglia showed a monotonic negative association with age thereafter; there was no significant association between age and the volumes of the thalamus, amygdala and the hippocampus (with some degree of decline in thalamus) until the sixth decade of life after which they also showed a steep negative association with age. The lateral ventricles showed continuous enlargement throughout the lifespan. Age was positively associated with inter-individual variability in the hippocampus and amygdala and the lateral ventricles. These results were robust to potential confounders and could be used to examine the functional significance of deviations from typical age-related morphometric patterns.
Keywords: ENIGMA; brain morphometry; longitudinal trajectories; multisite.
© 2021 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
H.‐J. G.: Travel grants and speaker honoraria from Fresenius Medical Care, Neuraxpharm, Servier and Janssen Cilag; research funding from Fresenius Medical Care. O. A. A.: Consultant to HealthLytix, speaker honorarium from Lundbeck. A. M. D.: Founder and member of the Scientific Advisory Board CorTechs Labs, Inc where he holds equity; member of the Scientific Advisory of Human Longevity Inc; research grants with General Electric Healthcare.
Figures


References
-
- Calabresi, P. , Picconi, B. , Tozzi, A. , Ghiglieri, V. , & Di Filippo, M. (2014). Direct and indirect pathways of basal ganglia: A critical reappraisal. Nature Neuroscience, 17, 1022–1030. - PubMed
-
- Chudasama, Y. , & Robbins, T. W. (2006). Functions of frontostriatal systems in cognition: Comparative neuropsychopharmacological studies in rats, monkeys and humans. Biological Psychology, 73, 19–38. - PubMed
-
- Cole, T. J. , & Green, P. J. (1992). Smoothing reference centile curves: The LMS method and penalized likelihood. Statistics in Medicine, 11, 1305–1319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG058854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH117014/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG068057/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH104284/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH116147/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH129742/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 EB020403/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH117014/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000153/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019771/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MH104284/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- P30 AG10133/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 1 U24 RR021992/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- MH116147/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- ERC_/European Research Council/International
- RO1HD050735/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000153/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH113619/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH120080/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH113619/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD050735/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- G0500092/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UL1 TR001414/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 RR021992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH042191/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH042191/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG060610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA101318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG19771/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH119219/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_17209/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U24 RR025736/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1 U24 RR025736-01/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DA029475/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

