Structural insights into the human D1 and D2 dopamine receptor signaling complexes
- PMID: 33571431
- PMCID: PMC8215686
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.027
Structural insights into the human D1 and D2 dopamine receptor signaling complexes
Abstract
The D1- and D2-dopamine receptors (D1R and D2R), which signal through Gs and Gi, respectively, represent the principal stimulatory and inhibitory dopamine receptors in the central nervous system. D1R and D2R also represent the main therapeutic targets for Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and many other neuropsychiatric disorders, and insight into their signaling is essential for understanding both therapeutic and side effects of dopaminergic drugs. Here, we report four cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of D1R-Gs and D2R-Gi signaling complexes with selective and non-selective dopamine agonists, including two currently used anti-Parkinson's disease drugs, apomorphine and bromocriptine. These structures, together with mutagenesis studies, reveal the conserved binding mode of dopamine agonists, the unique pocket topology underlying ligand selectivity, the conformational changes in receptor activation, and potential structural determinants for G protein-coupling selectivity. These results provide both a molecular understanding of dopamine signaling and multiple structural templates for drug design targeting the dopaminergic system.
Keywords: D1R; D2R; G protein selectivity; Parkinson’s disease; apomorphine; bromocriptine; cryo-EM; dopamine receptors; ligand selectivity; receptor activation.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
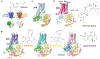
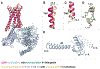

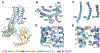



Comment in
-
Novel Cryo-EM structures of the D1 dopamine receptor unlock its therapeutic potential.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 May 22;6(1):205. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00630-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34023856 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Andersen PH, and Jansen JA (1990). Dopamine receptor agonists: selectivity and dopamine D1 receptor efficacy. Eur. J. Pharmacol 188, 335–347. - PubMed
-
- Ballesteros JA, and Weinstein H (1995). Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G protein-coupled receptors. In Methods in Neurosciences, Sealfon SC, ed. (Elsevier; ), pp. 366–428.
-
- Beaulieu JM, and Gainetdinov RR (2011). The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev 63, 182–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

