Crowded organelles, lipid accumulation, and abnormal membrane tubulation in cellular models of enhanced α-synuclein membrane interaction
- PMID: 33571519
- PMCID: PMC7988302
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147349
Crowded organelles, lipid accumulation, and abnormal membrane tubulation in cellular models of enhanced α-synuclein membrane interaction
Abstract
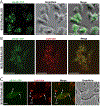
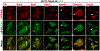
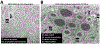
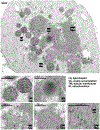
Previous work from our group showed that certain engineered missense mutations to the α-synuclein (αS) KTKEGV repeat motifs abrogate the protein's ability to form native multimers. The resultant excess monomers accumulate in lipid-membrane-rich inclusions associated with neurotoxicity exceeding that of natural familial Parkinson's disease mutants such as E46K. We presented an initial characterization of the lipid-rich inclusions and found similarities to the αS- and vesicle-rich inclusions that form in baker's yeast when αS is expressed. We also discussed, with some caution, a possible role of membrane-rich inclusions as precursors to filamentous Lewy bodies, the widely accepted hallmark pathology of Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies. In the meantime, advances in the microscopic characterization of Lewy bodies have highlighted the presence of crowded organelles and lipid membranes in addition to αS accumulation. This prompted us to revisit the αS inclusions caused by our repeat motif variants in neuroblastoma cells. In addition to our previous characterization, we found that these inclusions can often be seen by brightfield microscopy, overlap with endogenous vesicle markers in immunofluorescence experiments, stain positive for lipid dyes, and can be found to be closely associated with mitochondria. We also observed abnormal tubulation of membranes, which was subtle in inducible lines and pronounced in cells that transiently expressed high amounts of the highly disruptive KTKEGV motif mutant "KLKEGV". Membrane tubulation had been reported before as an αS activity in reductionist systems. Our in-cellulo demonstration now suggests that this mechanism could possibly be a relevant aspect of aberrant αS behavior in cells.
Keywords: Alpha-synuclein; Lipids; Parkinson’s disease; Vesicle trafficking.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell models of lipid-rich α-synuclein aggregation validate known modifiers of α-synuclein biology and identify stearoyl-CoA desaturase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Oct 8;116(41):20760-20769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1903216116. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31548371 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of native α-synuclein multimerization by strategically mutating its amphipathic helix causes abnormal vesicle interactions in neuronal cells.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Sep 15;26(18):3466-3481. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx227. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28911198 Free PMC article.
-
KTKEGV repeat motifs are key mediators of normal α-synuclein tetramerization: Their mutation causes excess monomers and neurotoxicity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Aug 4;112(31):9596-601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1505953112. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26153422 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicle trafficking and lipid metabolism in synucleinopathy.Acta Neuropathol. 2021 Apr;141(4):491-510. doi: 10.1007/s00401-020-02177-z. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Acta Neuropathol. 2021. PMID: 32607605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
α-Synuclein and Lewy pathology in Parkinson's disease.Curr Opin Neurol. 2015 Aug;28(4):375-81. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000215. Curr Opin Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26110807 Review.
Cited by
-
Excess membrane binding of monomeric alpha-, beta- and gamma-synuclein is invariably associated with inclusion formation and toxicity.Hum Mol Genet. 2021 Nov 16;30(23):2332-2346. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab188. Hum Mol Genet. 2021. PMID: 34254125 Free PMC article.
-
SCD Inhibition Protects from α-Synuclein-Induced Neurotoxicity But Is Toxic to Early Neuron Cultures.eNeuro. 2021 Aug 9;8(4):ENEURO.0166-21.2021. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0166-21.2021. Print 2021 Jul-Aug. eNeuro. 2021. PMID: 34301719 Free PMC article.
-
Acute lipid droplet accumulation induced by the inhibition of the phospholipase DDHD2 does not affect the level, solubility, or phosphoserine-129 status of α-synuclein.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Jan 24;40(1):111. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01534-9. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 39853540
-
Rapid iPSC inclusionopathy models shed light on formation, consequence, and molecular subtype of α-synuclein inclusions.Neuron. 2024 Sep 4;112(17):2886-2909.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.06.002. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Neuron. 2024. PMID: 39079530 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic Mechanisms of Cytosolic and Membrane-Enriched α-Synuclein Converge on Fatty Acid Homeostasis.J Neurosci. 2022 Mar 9;42(10):2116-2130. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1881-21.2022. Epub 2022 Jan 27. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35086904 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

