Leflunomide an immunomodulator with antineoplastic and antiviral potentials but drug-induced liver injury: A comprehensive review
- PMID: 33571819
- PMCID: PMC7869628
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107398
Leflunomide an immunomodulator with antineoplastic and antiviral potentials but drug-induced liver injury: A comprehensive review
Abstract
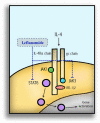
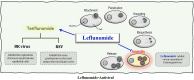
Leflunomide (LF) represents the prototype member of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) enzyme inhibitors. DHODH is a mitochondrial inner membrane enzyme responsible for catalytic conversion of dihydroorotate into orotate, a rate-limiting step in the de novo synthesis of the pyrimidine nucleotides. LF produces cellular depletion of pyrimidine nucleotides required for cell growth and proliferation. Based on the affected cells the outcome can be attainable as immunosuppression, antiproliferative, and/or the recently gained attention of the antiviral potentials of LF and its new congeners. Also, protein tyrosine kinase inhibition is an additional mechanistic benefit of LF, which inhibits immunological events such as cellular expansion and immunoglobulin production with an enhanced release of immunosuppressant cytokines. LF is approved for the treatment of autoimmune arthritis of rheumatoid and psoriatic pathogenesis. Also, LF has been used off-label for the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. However, LF antiviral activity is repurposed and under investigation with related compounds under a phase-I trial as a SARS CoV-2 antiviral in cases with COVID-19. Despite success in improving patients' mobility and reducing joint destruction, reported events of LF-induced liver injury necessitated regulatory precautions. LF should not be used in patients with hepatic impairment or in combination with drugs elaborating a burden on the liver without regular monitoring of liver enzymes and serum bilirubin as safety biomarkers. This study aims to review the pharmacological and safety profile of LF with a focus on the LF-induced hepatic injury from the perspective of pathophysiology and possible protective agents.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Antineoplastic; Antiviral; COVID-19; Drug-induced liver injury; Immunomodulator; Leflunomide.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no knowSn competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Sanofi-aventis: ARAVA® Tablets (leflunomide) 10 mg, 20 mg, 100 mg http://products.sanofi.us/arava/Arava.html, June 2020. In. Edited by Aventis S, vol. LEF-FPLR-SL-FEB16: Sanofi Aventis, 2016, pp. 1–25.
-
- Bartlett R.R., Schleyerbach R. Immunopharmacological profile of a novel isoxazol derivative, HWA 486, with potential antirheumatic activity–I. Disease modifying action on adjuvant arthritis of the rat. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1985;7(1):7–18. - PubMed
-
- Mattar T., Kochhar K., Bartlett R., Bremer E.G., Finnegan A. Inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase activity by leflunomide. FEBS Lett. 1993;334(2):161–164. - PubMed
-
- Williams J.W., Xiao F., Foster P.F., Chong A., Sharma S., Bartlett R., Sankary H.N. Immunosuppressive effects of leflunomide in a cardiac allograft model. Transpl. Proc. 1993;25(1 Pt 1):745–746. - PubMed
-
- Chong A.S., Zeng H., Knight D.A., Shen J., Meister G.T., Williams J.W., Waldman W.J. Concurrent antiviral and immunosuppressive activities of leflunomide in vivo. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transplant Surgeons. 2006;6(1):69–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

