Plant-Based Phenolic Molecules as Natural Preservatives in Comminuted Meats: A Review
- PMID: 33572049
- PMCID: PMC7915777
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10020263
Plant-Based Phenolic Molecules as Natural Preservatives in Comminuted Meats: A Review
Abstract
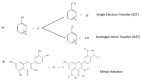
Comminuted meat products are highly susceptible to safety and quality degradation partly because of their large interfacial area in the emulsion. The food industry extensively uses synthetic chemical preservatives to delay that degradation which is caused by microbial growth, enzyme activities and oxidation reactions. However, due to the potential health damage (e.g., cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, cancers among others) synthetic preservatives in meat may cause, consumers are becoming skeptical to buy meat products containing such additives. In the meat industry, the interest of finding natural food preservatives is intensifying. Polyphenolic-rich plants used as natural food preservatives offer the best alternative for a partial or a complete replacement of their synthetic counterparts. They can be extracted from natural sources such as olives, fruits, grapes, vegetables, spices, herbs, and algae, and among others. The common feature of these phenolic compounds is that they have one or more aromatic rings with one or more -OH group which are essential for their antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. This review article is intended to provide an overview of the plant-based phenolic molecules used as natural food preservative, their antimicrobial and antioxidant mechanism of action, and their potential application in comminuted meat.
Keywords: antimicrobial; antioxidant; comminuted meat; natural preservatives; plant extracts; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- FAO . The State of Food Insecurity in the World Addressing Food Insecurity in Protracted Crises. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Rome, Italy: 2010.
-
- Berton-Carabin C.C., Ropers M.-H., Genot C. Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Involvement of the Interfacial Layer. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014;13:945–977. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12097. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

