Allosteric Interactions between Adenosine A2A and Dopamine D2 Receptors in Heteromeric Complexes: Biochemical and Pharmacological Characteristics, and Opportunities for PET Imaging
- PMID: 33572077
- PMCID: PMC7915359
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22041719
Allosteric Interactions between Adenosine A2A and Dopamine D2 Receptors in Heteromeric Complexes: Biochemical and Pharmacological Characteristics, and Opportunities for PET Imaging
Abstract
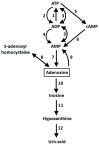
Adenosine and dopamine interact antagonistically in living mammals. These interactions are mediated via adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 receptors (R). Stimulation of A2AR inhibits and blockade of A2AR enhances D2R-mediated locomotor activation and goal-directed behavior in rodents. In striatal membrane preparations, adenosine decreases both the affinity and the signal transduction of D2R via its interaction with A2AR. Reciprocal A2AR/D2R interactions occur mainly in striatopallidal GABAergic medium spiny neurons (MSNs) of the indirect pathway that are involved in motor control, and in striatal astrocytes. In the nucleus accumbens, they also take place in MSNs involved in reward-related behavior. A2AR and D2R co-aggregate, co-internalize, and co-desensitize. They are at very close distance in biomembranes and form heteromers. Antagonistic interactions between adenosine and dopamine are (at least partially) caused by allosteric receptor-receptor interactions within A2AR/D2R heteromeric complexes. Such interactions may be exploited in novel strategies for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, substance abuse, and perhaps also attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Little is known about shifting A2AR/D2R heteromer/homodimer equilibria in the brain. Positron emission tomography with suitable ligands may provide in vivo information about receptor crosstalk in the living organism. Some experimental approaches, and strategies for the design of novel imaging agents (e.g., heterobivalent ligands) are proposed in this review.
Keywords: GABAergic enkephalinergic neuron; adenosine A2A receptor; allosteric interaction; dopamine D2 receptor; heteromers; receptor–receptor interactions; striatum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Allosteric mechanisms within the adenosine A2A-dopamine D2 receptor heterotetramer.Neuropharmacology. 2016 May;104:154-60. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.05.028. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26051403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allosteric interactions between agonists and antagonists within the adenosine A2A receptor-dopamine D2 receptor heterotetramer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jul 7;112(27):E3609-18. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1507704112. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26100888 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Control of the Function of the Striatopallidal Neuron by Pre-coupled Complexes of Adenosine A2A-Dopamine D2 Receptor Heterotetramers and Adenylyl Cyclase.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Apr 9;9:243. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00243. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29686613 Free PMC article.
-
Acute cocaine treatment enhances the antagonistic allosteric adenosine A2A-dopamine D2 receptor-receptor interactions in rat dorsal striatum without increasing significantly extracellular dopamine levels.Pharmacol Rep. 2020 Apr;72(2):332-339. doi: 10.1007/s43440-020-00069-3. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Pharmacol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32124388
-
Understanding the Functional Plasticity in Neural Networks of the Basal Ganglia in Cocaine Use Disorder: A Role for Allosteric Receptor-Receptor Interactions in A2A-D2 Heteroreceptor Complexes.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:4827268. doi: 10.1155/2016/4827268. Epub 2016 Oct 30. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 27872762 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dopamine D2 and Adenosine A2A Receptors Interaction on Ca2+ Current Modulation in a Rodent Model of Parkinsonism.ASN Neuro. 2022 Jan-Dec;14:17590914221102075. doi: 10.1177/17590914221102075. ASN Neuro. 2022. PMID: 36050845 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric Regulation of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: From Diversity of Molecular Mechanisms to Multiple Allosteric Sites and Their Ligands.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 24;24(7):6187. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076187. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocyte regulation of synaptic signaling in psychiatric disorders.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023 Jan;48(1):21-36. doi: 10.1038/s41386-022-01338-w. Epub 2022 May 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 35577914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Intracerebral Aminophylline Dosing on Catalepsy and Gait in an Animal Model of Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 10;25(10):5191. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105191. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791229 Free PMC article.
-
Ketogenic diet, adenosine, and dopamine in addiction and psychiatry.Front Nutr. 2025 Mar 10;12:1492306. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1492306. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40129664 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

