Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance of Commercial Stainless Steel Used in Dental Instruments
- PMID: 33572235
- PMCID: PMC7915631
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14040827
Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance of Commercial Stainless Steel Used in Dental Instruments
Abstract
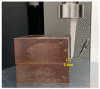
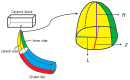
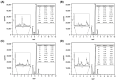
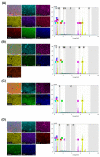
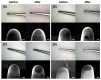
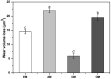
The aim of this study was to investigate the element composition and grain size of commercial dental instruments used for ultrasonic scaler tips, which are composed of stainless-steel materials. The differences in mechanical properties and wear resistances were compared. The samples were classified into 4 groups in accordance with the manufacturer, Electro Medical Systems, 3A MEDES, DMETEC and OSUNG MND, and the element compositions of each stainless-steel ultrasonic scaler tip were analyzed with micro-X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (μXRF) and field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). One-way ANOVA showed that there were significant differences in shear strength and Vickers hardness among the stainless-steel ultrasonic scaler tips depending on the manufacturer (p < 0.05). The mass before and after wear were found to have no significant difference among groups (p > 0.05), but there was a significant difference in the wear volume loss (p < 0.05). The results were then correlated with μXRF results as well as observations of grain size with optical microscopy, which concluded that the Fe content and the grain size of the stainless steel have significant impacts on strength. Additionally, stainless-steel ultrasonic scaler tips with higher Vickers hardness values showed greater wear resistance, which would be an important wear characteristic for clinicians to check.
Keywords: Vickers hardness; dental instrument; stainless steel; ultrasonic scaler tip; wear resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the safety and efficiency of novel metallic ultrasonic scaler tip on titanium surfaces.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012 Nov;23(11):1269-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02302.x. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012. PMID: 22093039
-
Evaluation of the safety and efficiency of novel metallic implant scaler tips manufactured by the powder injection molding technique.BMC Oral Health. 2017 Jul 11;17(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12903-017-0396-z. BMC Oral Health. 2017. PMID: 28697771 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical coloring on stainless steel by ultrasonic irradiation.Ultrason Sonochem. 2018 Jan;40(Pt A):558-566. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.07.049. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Ultrason Sonochem. 2018. PMID: 28946458
-
Boronization and Carburization of Superplastic Stainless Steel and Titanium-Based Alloys.Materials (Basel). 2011 Jul 18;4(7):1309-1320. doi: 10.3390/ma4071309. Materials (Basel). 2011. PMID: 28824144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Surface Nanocrystallization on Wear Behavior of Steels: A Review.Materials (Basel). 2024 Apr 1;17(7):1618. doi: 10.3390/ma17071618. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38612132 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In-vitro effects of novel periodontal scalers with a planar ultrasonic piezoelectric transducer on periodontal biofilm removal, dentine surface roughness, and periodontal ligament fibroblasts adhesion.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 May 3;28(5):294. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05671-w. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 38698252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gherlone E.F., Capparé P., Tecco S., Polizzi E., Pantaleo G., Gastaldi G., Grusovin M.G. A Prospective Longitudinal Study on Implant Prosthetic Rehabilitation in Controlled HIV-Positive Patients with 1-Year Follow-Up: The Role of CD4+ Level, Smoking Habits, and Oral Hygiene. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2015;18:955–964. doi: 10.1111/cid.12370. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

