The Assessment of Risk and Predictors of Sleep Disorders in Patients with Psoriasis-A Questionnaire-Based Cross-Sectional Analysis
- PMID: 33572270
- PMCID: PMC7916004
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10040664
The Assessment of Risk and Predictors of Sleep Disorders in Patients with Psoriasis-A Questionnaire-Based Cross-Sectional Analysis
Abstract
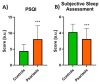
Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory skin disease affecting 2-4% of the general population. Accompanying subjective symptoms (pruritus or pain) may cause decreased life quality including sleep disorders (SD). Sixty psoriatic patients fulfilled the following questionnaires: Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), STOP BANG for the obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) assessment, and Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) Severity Scale. Patients' laboratory and clinical data were also investigated. All data obtained were compared to 40 participants without dermatoses. Mean PSQI, risk of OSAS, and RLS severity of psoriatics were significantly higher than in controls (p < 0.0001, p < 0.05, p < 0.05 respectively). There was a positive correlation between the time of suffering from psoriasis and the risk of OSAS (R = 0.286, p < 0.05). We did not observe any significant relationship between PSQI, risk of OSAS, or RLS and psoriasis severity assessed with PASI (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index). We identified four possible predictors of RLS: glucose, CRP and total cholesterol concentrations, and PSQI. SD are significantly more frequent in psoriatics than in people without chronic dermatological diseases but surprisingly they are not correlated with psoriasis severity. SD decrease patients' life quality and may result in serious consequences. Therefore, establishing recommendations concerning screening for SD and their predictors should be considered.
Keywords: PSQI; Pittsburgh sleep quality index; RLS; STOP BANG; obstructive sleep apnea syndrome; psoriasis; restless legs syndrome; sleep disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Restless legs syndrome in patients with psoriasis: association with inflammation and sleep quality.Int J Dermatol. 2023 Apr;62(4):501-507. doi: 10.1111/ijd.16532. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Int J Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36468846
-
Sleep disorders in patients with psoriasis: a cross-sectional study using non-polysomnographical methods.Sleep Breath. 2019 Sep;23(3):893-898. doi: 10.1007/s11325-019-01820-8. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Sleep Breath. 2019. PMID: 30859369
-
Restless Legs Syndrome in Psoriasis: A Multicenter Study on Its Prevalence, Severity, and Impact on Patients.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2025 Feb 13;18:367-378. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S502902. eCollection 2025. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39968328 Free PMC article.
-
Restless legs syndrome in end-stage renal disease.Sleep Med. 2004 May;5(3):309-15. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2004.01.014. Sleep Med. 2004. PMID: 15165541 Review.
-
Iron for the treatment of restless legs syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 4;1(1):CD007834. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007834.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30609006 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mutual Relationship Between Sleep Disorders, Quality of Life and Psychosocial Aspects in Patients With Psoriasis.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 6;12:674460. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.674460. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34295272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Management of Psoriasis Complicated with Depression.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 May 18;16:1287-1301. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S413887. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37223217 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Lifestyle Changes on Disease Severity and Quality of Life in Patients with Plaque Psoriasis: A Narrative Review.Psoriasis (Auckl). 2022 Apr 9;12:35-51. doi: 10.2147/PTT.S294189. eCollection 2022. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2022. PMID: 35433402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep behaviour differs in women and men with psoriatic arthritis and axial spondyloarthritis with impact on quality of life and depressive symptoms.RMD Open. 2023 May;9(2):e002912. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002912. RMD Open. 2023. PMID: 37208029 Free PMC article.
-
Subclinical Cardiac Organ Damage in Patients with Moderate to Severe Psoriasis.J Clin Med. 2021 May 31;10(11):2440. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112440. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34072722 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

