Structural Basis of the Pore-Forming Toxin/Membrane Interaction
- PMID: 33572271
- PMCID: PMC7914777
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins13020128
Structural Basis of the Pore-Forming Toxin/Membrane Interaction
Abstract
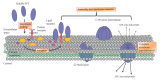
With the rapid growth of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, it is urgent to develop alternative therapeutic strategies. Pore-forming toxins (PFTs) belong to the largest family of virulence factors of many pathogenic bacteria and constitute the most characterized classes of pore-forming proteins (PFPs). Recent studies revealed the structural basis of several PFTs, both as soluble monomers, and transmembrane oligomers. Upon interacting with host cells, the soluble monomer of bacterial PFTs assembles into transmembrane oligomeric complexes that insert into membranes and affect target cell-membrane permeability, leading to diverse cellular responses and outcomes. Herein we have reviewed the structural basis of pore formation and interaction of PFTs with the host cell membrane, which could add valuable contributions in comprehensive understanding of PFTs and searching for novel therapeutic strategies targeting PFTs and interaction with host receptors in the fight of bacterial antibiotic-resistance.
Keywords: membrane interaction; pore-forming toxin; structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Taking Toll on Membranes: Curious Cases of Bacterial β-Barrel Pore-Forming Toxins.Biochemistry. 2020 Jan 21;59(2):163-170. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00783. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 31608629 Review.
-
Bacterial pore-forming toxins.Microbiology (Reading). 2022 Mar;168(3):001154. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001154. Microbiology (Reading). 2022. PMID: 35333704 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis and Functional Implications of the Membrane Pore-Formation Mechanisms of Bacterial Pore-Forming Toxins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1112:281-291. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-3065-0_19. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30637704 Review.
-
Pore-forming toxins: ancient, but never really out of fashion.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Feb;14(2):77-92. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2015.3. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26639780 Review.
-
Cryo-EM elucidates mechanism of action of bacterial pore-forming toxins.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2022 Nov 1;1864(11):184013. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2022.184013. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2022. PMID: 35908609
Cited by
-
The choanoflagellate pore-forming lectin SaroL-1 punches holes in cancer cells by targeting the tumor-related glycosphingolipid Gb3.Commun Biol. 2022 Sep 12;5(1):954. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03869-w. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36097056 Free PMC article.
-
Small Proteins; Big Questions.J Bacteriol. 2022 Jan 18;204(1):e0034121. doi: 10.1128/JB.00341-21. Epub 2021 Jul 26. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 34309401 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Analysis of Membrane-associated Forms of Helicobacter pylori VacA Toxin.J Mol Biol. 2024 Feb 15;436(4):168432. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168432. Epub 2023 Dec 30. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38161000 Free PMC article.
-
Pore-Forming Proteins: From Pore Assembly to Structure by Quantitative Single-Molecule Imaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 25;24(5):4528. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054528. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Simple Radioassay to Detect Nanoscale Membrane Disruption.Methods Protoc. 2023 Feb 25;6(2):23. doi: 10.3390/mps6020023. Methods Protoc. 2023. PMID: 36961043 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

