Potential Whole-Cell Biosensors for Detection of Metal Using MerR Family Proteins from Enterobacter sp. YSU and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia OR02
- PMID: 33572806
- PMCID: PMC7911910
- DOI: 10.3390/mi12020142
Potential Whole-Cell Biosensors for Detection of Metal Using MerR Family Proteins from Enterobacter sp. YSU and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia OR02
Abstract
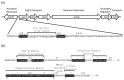
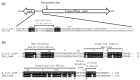
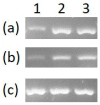
Cell-based biosensors harness a cell's ability to respond to the environment by repurposing its sensing mechanisms. MerR family proteins are activator/repressor switches that regulate the expression of bacterial metal resistance genes and have been used in metal biosensors. Upon metal binding, a conformational change switches gene expression from off to on. The genomes of the multimetal resistant bacterial strains, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Oak Ridge strain 02 (S. maltophilia 02) and Enterobacter sp. YSU, were recently sequenced. Sequence analysis and gene cloning identified three mercury resistance operons and three MerR switches in these strains. Transposon mutagenesis and sequence analysis identified Enterobacter sp. YSU zinc and copper resistance operons, which appear to be regulated by the protein switches, ZntR and CueR, respectively. Sequence analysis and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) showed that a CueR switch appears to activate a S. maltophilia 02 copper transport gene in the presence of CuSO4 and HAuCl4·3H2O. In previous studies, genetic engineering replaced metal resistance genes with the reporter genes for β-galactosidase, luciferase or the green fluorescence protein (GFP). These produce a color change of a reagent, produce light, or fluoresce in the presence of ultraviolet (UV) light, respectively. Coupling these discovered operons with reporter genes has the potential to create whole-cell biosensors for HgCl2, ZnCl2, CuSO4 and HAuCl4·3H2O.
Keywords: CuSO4; CueR; Enterobacter; HAuCl4·3H2O; HgCl2; MerR family protein; Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; ZnCl2; ZntR; bacterial metal resistance; whole-cell biosensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of two multimetal resistant bacterial strains: Enterobacter sp. YSU and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia ORO2.Curr Microbiol. 2009 Nov;59(5):526-31. doi: 10.1007/s00284-009-9471-2. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Curr Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19688378
-
Multidrug-resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: Description of new MLST profiles and resistance and virulence genes using whole-genome sequencing.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2018 Dec;15:212-214. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 20. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2018. PMID: 30036694
-
Engineering and characterization of copper and gold sensors in Escherichia coli and Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Mar;103(6):2797-2808. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9490-7. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30645690
-
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia drug resistance.Future Microbiol. 2009 Aug;4(6):655-60. doi: 10.2217/fmb.09.45. Future Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19659422 Review.
-
Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: a review of current knowledge.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2020 Apr;18(4):335-347. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1730178. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2020. PMID: 32052662 Review.
Cited by
-
Draft genome analysis for Enterobacter kobei, a promising lead bioremediation bacterium.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 8;11:1335854. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1335854. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38260751 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Transcription Factor-Based Biosensors: Innovations from Design to Applications in Synthetic Biology.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;15(4):221. doi: 10.3390/bios15040221. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40277535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Draft genome of Raoultella planticola, a high lead resistance bacterium from industrial wastewater.AMB Express. 2023 Jan 30;13(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13568-023-01519-w. AMB Express. 2023. PMID: 36715862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jouanneau S., Durand M.-J., Courcoux P., Blusseau T., Thouand G. Improvement of the identification of four heavy metals in environmental samples by using predictive decision tree models coupled with a set of five bioluminescent bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011;45:2925–2931. doi: 10.1021/es1031757. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

