The Influence of the Extremely Low Frequency Electromagnetic Field on Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma
- PMID: 33572811
- PMCID: PMC7866299
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22031342
The Influence of the Extremely Low Frequency Electromagnetic Field on Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma
Abstract
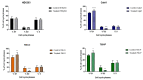
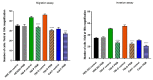
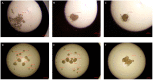
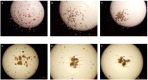
The development of new technologies and industry is conducive to the increase in the number and variety of electromagnetic field (EMF) sources in our environment. The main sources of EMF are high-voltage lines, household appliances, audio/video devices, mobile phones, radio stations, and radar devices. In the growing use of electronic devices, scientists are increasingly interested in the effects of EMF on human health. Even though many studies on the effects of EMF have already been carried out, none of them has shown a significant effect on mammals, including humans. Moreover, it is not entirely clear how EMF influences cell behavior. The International Agency for Research on Cancer on 31 May 2011, classified PEM as a possible carcinogenic factor. This study aimed to investigate the effect of the electromagnetic field on morphological and functional changes in clear cell renal carcinoma. The research was carried out on in vitro cultures of four cell lines: HEK293, 786-O 769-P, and Caki1. The results of the research showed that the EMF of low frequency had a slight effect on the viability of cells. EMF, which induced cell arrest in the G1 phase, increased the number of early apoptotic cells and decreased the number of viable cells in the 786-O line. EMF did not affect the proliferation and viability of HEK293 cells. Extreme low-frequency EMF (ELF-EMF) also showed an inhibitory effect on the migration and metastatic properties of clear cell kidney cancer cells. Moreover, shortly after the end of ELF-EMF exposure, significant increases in ROS levels were observed in all tested cell lines. As part of the work, it was shown that low-frequency EMF shows an inhibitory effect on the proliferation of primary cancer cells, diminishing their migratory, invasive, and metastatic abilities. It also increases the apoptosis of cancer cells and the amount of reactive oxygen species. Based on the results of our research, we want to point up that the effect of ELF-EMF depends on a specific metabolic state or at a specific stage in the cell cycle of the cells under study.
Keywords: EMF; cancer; ccRCC; electromagnetic field; kidney; renal carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field (ELF-EMF) induced alterations in gene expression and cytokine secretion in clear cell renal carcinoma cells.Med Pr. 2024 May 21;75(2):133-141. doi: 10.13075/mp.5893.01476. Epub 2024 May 8. Med Pr. 2024. PMID: 38717134
-
Neuroprotective effects of lotus seedpod procyanidins on extremely low frequency electromagnetic field-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured hippocampal neurons.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Aug;82:628-39. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.05.032. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27470406
-
EUROPAEM EMF Guideline 2016 for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of EMF-related health problems and illnesses.Rev Environ Health. 2016 Sep 1;31(3):363-97. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2016-0011. Rev Environ Health. 2016. PMID: 27454111 Review.
-
Effect of extremely low frequency electromagnetic field parameters on the proliferation of human breast cancer.Electromagn Biol Med. 2021 Jul 3;40(3):384-392. doi: 10.1080/15368378.2021.1891093. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Electromagn Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33632057
-
Cell type specific redox status is responsible for diverse electromagnetic field effects.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(10):1141-52. doi: 10.2174/092986707780362835. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17456027 Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetic Fields and Cancer: Epidemiology, Cellular Biology, and Theranostics.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 25;23(3):1339. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031339. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mechanistically approached review upon assorted cell lines stimulated by athermal electromagnetic irradiation.Cell Cycle. 2023 Jun;22(11):1319-1342. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2023.2206682. Epub 2023 May 5. Cell Cycle. 2023. PMID: 37144743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of short-term extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field on respiratory functions.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2025 Jun 2;71(4):e20241812. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20241812. eCollection 2025. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2025. PMID: 40465999 Free PMC article.
-
Low-intensity continuous ultrasound to inhibit cancer cell migration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 12;10:842965. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.842965. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36712968 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields on Pain, Stiffness, and Physical Function in Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Pain Res Manag. 2022 May 9;2022:9939891. doi: 10.1155/2022/9939891. eCollection 2022. Pain Res Manag. 2022. PMID: 35586276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stewart B.W., Wild C. World Cancer Report 2014. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2014.
-
- Provenzano A.E., Amatori S., Nasoni M.G., Persico G., Russo S., Mastrogiacomo A.R., Gambarara A., Fanelli M. Effects of Fifty-Hertz Electromagnetic Fields on Granulocytic Differentiation of ATRA-Treated Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia NB4 Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018;46:389–400. doi: 10.1159/000488473. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

