Staphylococcal Biofilms: Challenges and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives
- PMID: 33573022
- PMCID: PMC7911828
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10020131
Staphylococcal Biofilms: Challenges and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives
Abstract
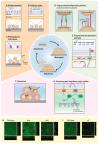
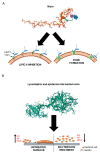
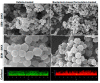
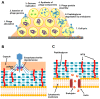
Staphylococci, like Staphylococcus aureus and S. epidermidis, are common colonizers of the human microbiota. While being harmless in many cases, many virulence factors result in them being opportunistic pathogens and one of the major causes of hospital-acquired infections worldwide. One of these virulence factors is the ability to form biofilms-three-dimensional communities of microorganisms embedded in an extracellular polymeric matrix (EPS). The EPS is composed of polysaccharides, proteins and extracellular DNA, and is finely regulated in response to environmental conditions. This structured environment protects the embedded bacteria from the human immune system and decreases their susceptibility to antimicrobials, making infections caused by staphylococci particularly difficult to treat. With the rise of antibiotic-resistant staphylococci, together with difficulty in removing biofilms, there is a great need for new treatment strategies. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of our current knowledge of the stages of biofilm development and what difficulties may arise when trying to eradicate staphylococcal biofilms. Furthermore, we look into promising targets and therapeutic methods, including bacteriocins and phage-derived antibiofilm approaches.
Keywords: S. aureus; antibiotics; bacteriocins; bacteriophages; biofilm; coagulase-negative staphylococci.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibacterial Effects of Phage Lysin LysGH15 on Planktonic Cells and Biofilms of Diverse Staphylococci.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jul 17;84(15):e00886-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00886-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29776929 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecules Produced by Commensal Staphylococcus epidermidis Disrupt Formation of Biofilms by Staphylococcus aureus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Feb 18;86(5):e02539-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02539-19. Print 2020 Feb 18. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31862721 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of bacteriophages for staphylococcal infections and selected methods for in vitro susceptibility testing of staphylococci.Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2020 Winter;69(1):10-18. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2020. PMID: 32326711 English.
-
Fighting biofilms with lantibiotics and other groups of bacteriocins.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2018 Apr 19;4:9. doi: 10.1038/s41522-018-0053-6. eCollection 2018. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2018. PMID: 29707229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcal-Produced Bacteriocins and Antimicrobial Peptides: Their Potential as Alternative Treatments for Staphylococcus aureus Infections.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Jan 21;9(2):40. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9020040. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31973108 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aqueous Extracts from Hemp Seeds as a New Weapon against Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilms.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 7;24(22):16026. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216026. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003214 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence, Susceptibility Profile, and Clinical Characteristics of Pathogenic Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci.Cureus. 2024 Aug 7;16(8):e66397. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66397. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39247021 Free PMC article.
-
Pentadecanoic Acid-Releasing PDMS: Towards a New Material to Prevent S. epidermidis Biofilm Formation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 5;25(19):10727. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910727. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409056 Free PMC article.
-
New Imidazolium Alkaloids with Broad Spectrum of Action from the Marine Bacterium Shewanella aquimarina.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 14;15(8):2139. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082139. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631353 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing understanding of microbial biofilms through machine learning-powered studies.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 28;32(12):1653-1664. doi: 10.1007/s10068-023-01415-w. eCollection 2023 Oct. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37780593 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Monegro A.F., Muppidi V., Regunath H. Hospital Acquired Infections. In StatPearls; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2020. - PubMed
-
- Cassini A., Högberg L.D., Plachouras D., Quattrocchi A., Hoxha A., Simonsen G.S., Colomb-Cotinat M., E Kretzschmar M., Devleesschauwer B., Cecchini M., et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019;19:56–66. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

