Environmental Impact of Geosynthetics in Coastal Protection
- PMID: 33573061
- PMCID: PMC7866501
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14030634
Environmental Impact of Geosynthetics in Coastal Protection
Abstract
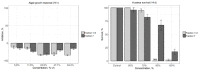
Geosynthetic materials are applied in measures for coastal protection. Weathering or any damage of constructions, as shown by a field study in Kaliningrad Oblast (Russia), could lead to the littering of the beach or the sea (marine littering) and the discharge of possibly harmful additives into the marine environment. The ageing behavior of a widely used geotextile made of polypropylene was studied by artificial accelerated ageing in water-filled autoclaves at temperatures of 30 to 80 °C and pressures of 10 to 50 bar. Tensile strength tests were used to evaluate the progress of ageing, concluding that temperature rather than pressure was the main factor influencing the ageing of geotextiles. Using a modified Arrhenius equation, it was possible to calculate the half-life for the loss of 50% of the strain, which corresponds to approximately 330 years. Dynamic surface leaching and ecotoxicological tests were performed to determine the possible release of contaminants. No harmful effects on the test organisms were observed.
Keywords: artificial ageing; dynamic surface leaching test; geosynthetics; geotextiles; marine littering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Geographical information dataset "geosynthetics in coastal protection of the South-East Baltic".Data Brief. 2021 Dec 8;40:107693. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2021.107693. eCollection 2022 Feb. Data Brief. 2021. PMID: 34977289 Free PMC article.
-
Dataset on geosynthetic material debris contamination of the South-East Baltic shore.Data Brief. 2022 Jan 1;40:107778. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2021.107778. eCollection 2022 Feb. Data Brief. 2022. PMID: 35028350 Free PMC article.
-
Weathering of a Nonwoven Polypropylene Geotextile: Field vs. Laboratory Exposure.Materials (Basel). 2022 Nov 18;15(22):8216. doi: 10.3390/ma15228216. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36431700 Free PMC article.
-
Geosynthetics in geoenvironmental engineering.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2015 May 8;16(3):034605. doi: 10.1088/1468-6996/16/3/034605. eCollection 2015 Jun. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2015. PMID: 27877792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric Products in Erosion Control Applications: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Aug 31;16(17):2490. doi: 10.3390/polym16172490. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39274123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Measurement of the Environmental Impact of Materials.Materials (Basel). 2022 Mar 17;15(6):2208. doi: 10.3390/ma15062208. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35329662 Free PMC article.
-
Geographical information dataset "geosynthetics in coastal protection of the South-East Baltic".Data Brief. 2021 Dec 8;40:107693. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2021.107693. eCollection 2022 Feb. Data Brief. 2021. PMID: 34977289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bandow N., Aitken M.D., Geburtig A., Kalbe U., Piechotta C., Schoknecht U., Simon F.-G., Stephan I. Using Environmental Simulations to Test the Release of Hazardous Substances from Polymer-Based Products: Are Realism and Pragmatism Mutually Exclusive Objectives? Materials. 2020;13:2709. doi: 10.3390/ma13122709. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Simon F.G., Wachtendorf V., Geburtig A., Trubiroha P. Materials and the environment, Environmental Impact of Materials. In: Czichos H., Saito T., Smith L., editors. Springer Handbook of Metrology and Testing. Springer; Heidelberg, Germany: 2011. pp. 845–860.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

