Extracellular Vesicles Do Not Mediate the Anti-Inflammatory Actions of Mouse-Derived Adipose Tissue Mesenchymal Stem Cells Secretome
- PMID: 33573086
- PMCID: PMC7866557
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22031375
Extracellular Vesicles Do Not Mediate the Anti-Inflammatory Actions of Mouse-Derived Adipose Tissue Mesenchymal Stem Cells Secretome
Abstract
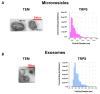
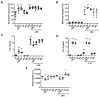
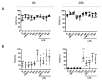
Adipose tissue represents an abundant source of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) for therapeutic purposes. Previous studies have demonstrated the anti-inflammatory potential of adipose tissue-derived MSC (ASC). Extracellular vesicles (EV) present in the conditioned medium (CM) have been shown to mediate the cytoprotective effects of human ASC secretome. Nevertheless, the role of EV in the anti-inflammatory effects of mouse-derived ASC is not known. The current study has investigated the influence of mouse-derived ASC CM and its fractions on the response of mouse-derived peritoneal macrophages against lipopolysaccharide (LPS). CM and its soluble fraction reduced the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, adenosine triphosphate and nitric oxide in stimulated cells. They also enhanced the migration of neutrophils or monocytes, in the absence or presence of LPS, respectively, which is likely related to the presence of chemokines, and reduced the phagocytic response. The anti-inflammatory effect of CM may be dependent on the regulation of toll-like receptor 4 expression and nuclear factor-κB activation. Our results demonstrate the anti-inflammatory effects of mouse-derived ASC secretome in mouse-derived peritoneal macrophages stimulated with LPS and show that they are not mediated by EV.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; inflammation; macrophage; mesenchymal stem cells secretome; mouse-derived adipose tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

