Impairment of Spike-Timing-Dependent Plasticity at Schaffer Collateral-CA1 Synapses in Adult APP/PS1 Mice Depends on Proximity of Aβ Plaques
- PMID: 33573114
- PMCID: PMC7866519
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22031378
Impairment of Spike-Timing-Dependent Plasticity at Schaffer Collateral-CA1 Synapses in Adult APP/PS1 Mice Depends on Proximity of Aβ Plaques
Abstract
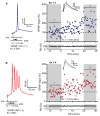
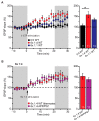
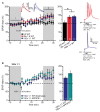
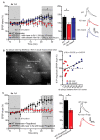
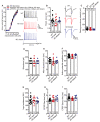
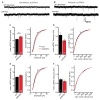
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a multifaceted neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive and irreversible cognitive decline, with no disease-modifying therapy until today. Spike timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) is a Hebbian form of synaptic plasticity, and a strong candidate to underlie learning and memory at the single neuron level. Although several studies reported impaired long-term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampus in AD mouse models, the impact of amyloid-β (Aβ) pathology on STDP in the hippocampus is not known. Using whole cell patch clamp recordings in CA1 pyramidal neurons of acute transversal hippocampal slices, we investigated timing-dependent (t-) LTP induced by STDP paradigms at Schaffer collateral (SC)-CA1 synapses in slices of 6-month-old adult APP/PS1 AD model mice. Our results show that t-LTP can be induced even in fully developed adult mice with different and even low repeat STDP paradigms. Further, adult APP/PS1 mice displayed intact t-LTP induced by 1 presynaptic EPSP paired with 4 postsynaptic APs (6× 1:4) or 1 presynaptic EPSP paired with 1 postsynaptic AP (100× 1:1) STDP paradigms when the position of Aβ plaques relative to recorded CA1 neurons in the slice were not considered. However, when Aβ plaques were live stained with the fluorescent dye methoxy-X04, we observed that in CA1 neurons with their somata <200 µm away from the border of the nearest Aβ plaque, t-LTP induced by 6× 1:4 stimulation was significantly impaired, while t-LTP was unaltered in CA1 neurons >200 µm away from plaques. Treatment of APP/PS1 mice with the anti-inflammatory drug fingolimod that we previously showed to alleviate synaptic deficits in this AD mouse model did not rescue the impaired t-LTP. Our data reveal that overexpression of APP and PS1 mutations in AD model mice disrupts t-LTP in an Aβ plaque distance-dependent manner, but cannot be improved by fingolimod (FTY720) that has been shown to rescue conventional LTP in CA1 of APP/PS1 mice.
Keywords: Alzheimer; FTY720; Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses; adult animals; amyloid beta plaques; fingolimod; timing-dependent LTP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-Inflammatory Treatment with FTY720 Starting after Onset of Symptoms Reverses Synaptic Deficits in an AD Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 25;21(23):8957. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238957. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33255764 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Synaptic Dysfunction Between rTg4510 and APP/PS1 Mouse Models of Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;61(1):195-208. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170457. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 29154272 Free PMC article.
-
The flavonoid baicalein rescues synaptic plasticity and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Sep 15;311:309-321. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.05.052. Epub 2016 May 24. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27233830
-
Presenilin transgenic mice as models of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Struct Funct. 2010 Mar;214(2-3):127-43. doi: 10.1007/s00429-009-0227-3. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Brain Struct Funct. 2010. PMID: 19921519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The upside of APP at synapses.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012 Jan;18(1):47-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00221.x. Epub 2010 Dec 27. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012. PMID: 21199446 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EK100 and Antrodin C Improve Brain Amyloid Pathology in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice by Promoting Microglial and Perivascular Clearance Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 27;22(19):10413. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910413. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638752 Free PMC article.
-
Protecting effects of 4-octyl itaconate on neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy via Nrf2 pathway in astrocytes.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 May 17;21(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03121-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38760862 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol modulates glutamate dynamics in the hippocampus of an animal model of Alzheimer's disease.Neurotherapeutics. 2024 Sep;21(5):e00439. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00439. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Neurotherapeutics. 2024. PMID: 39232876 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic plasticity in human thalamocortical assembloids.Cell Rep. 2024 Aug 27;43(8):114503. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114503. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39018245 Free PMC article.
-
From synapses to circuits and back: Bridging levels of understanding in animal models of Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Neurosci. 2022 Nov;56(9):5564-5586. doi: 10.1111/ejn.15636. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Eur J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35244297 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goedert M., Wischik C.M., Crowther R.A., Walker J.E., Klug A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding a core protein of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease: Identification as the microtubule-associated protein tau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1988;85:4051–4055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4051. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

