Addressable nanoantennas with cleared hotspots for single-molecule detection on a portable smartphone microscope
- PMID: 33574261
- PMCID: PMC7878865
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21238-9
Addressable nanoantennas with cleared hotspots for single-molecule detection on a portable smartphone microscope
Abstract
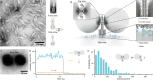
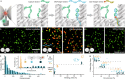
The advent of highly sensitive photodetectors and the development of photostabilization strategies made detecting the fluorescence of single molecules a routine task in many labs around the world. However, to this day, this process requires cost-intensive optical instruments due to the truly nanoscopic signal of a single emitter. Simplifying single-molecule detection would enable many exciting applications, e.g., in point-of-care diagnostic settings, where costly equipment would be prohibitive. Here, we introduce addressable NanoAntennas with Cleared HOtSpots (NACHOS) that are scaffolded by DNA origami nanostructures and can be specifically tailored for the incorporation of bioassays. Single emitters placed in NACHOS emit up to 461-fold (average of 89 ± 7-fold) brighter enabling their detection with a customary smartphone camera and an 8-US-dollar objective lens. To prove the applicability of our system, we built a portable, battery-powered smartphone microscope and successfully carried out an exemplary single-molecule detection assay for DNA specific to antibiotic-resistant Klebsiella pneumonia on the road.
Conflict of interest statement
P.T. and G.P.A. are inventors on an awarded patent of the described bottom-up method for fluorescence enhancement in molecular assays, EP1260316.1, 2012, US20130252825 A1. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

