Chromosome-scale genome assembly of the sea louse Caligus rogercresseyi by SMRT sequencing and Hi-C analysis
- PMID: 33574331
- PMCID: PMC7878743
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-021-00842-w
Chromosome-scale genome assembly of the sea louse Caligus rogercresseyi by SMRT sequencing and Hi-C analysis
Abstract
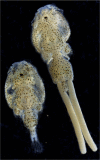
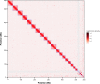
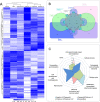
Caligus rogercresseyi, commonly known as sea louse, is an ectoparasite copepod that impacts the salmon aquaculture in Chile, causing losses of hundreds of million dollars per year. In this study, we report a chromosome-scale assembly of the sea louse (C. rogercresseyi) genome based on single-molecule real-time sequencing (SMRT) and proximity ligation (Hi-C) analysis. Coding RNAs and non-coding RNAs, and specifically long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) were identified through whole transcriptome sequencing from different life stages. A total of 23,686 protein-coding genes and 12,558 non-coding RNAs were annotated. In addition, 6,308 lncRNAs and 5,774 miRNAs were found to be transcriptionally active from larvae to adult stages. Taken together, this genomic resource for C. rogercresseyi represents a valuable tool to develop sustainable control strategies in the salmon aquaculture industry.
Conflict of interest statement
IL and BN are employees and shareholders of Phase Genomics, Inc, a company commercializing Hi-C technology.
Figures

References
-
- Costelloe M, Costelloe J, O’Donohoe G, Coghlan N, O’Connor B. A review of field studies on the sea louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis Kroyer on the west coast of Ireland. Bull Eur Assn Fish P. 1999;19:260–264.
-
- Gallardo-Escarate C, et al. The race between host and sea lice in the Chilean salmon farming: a genomic approach. Rev Aquacult. 2019;11:325–339. doi: 10.1111/raq.12334. - DOI
-
- Dresdner J, et al. Impact of Caligus treatments on unit costs of heterogeneous salmon farms in Chile. Aquacult Econ Manag. 2019;23:1–27. doi: 10.1080/13657305.2018.1449271. - DOI
-
- Abolofia J, Wilen JE, Asche F. The Cost of Lice: Quantifying the Impacts of Parasitic Sea Lice on Farmed Salmon. Mar Resour Econ. 2017;32:329–349. doi: 10.1086/691981. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

