BACH2 enforces the transcriptional and epigenetic programs of stem-like CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 33574619
- PMCID: PMC7906956
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-021-00868-7
BACH2 enforces the transcriptional and epigenetic programs of stem-like CD8+ T cells
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: BACH2 enforces the transcriptional and epigenetic programs of stem-like CD8+ T cells.Nat Immunol. 2021 Apr;22(4):530. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00906-4. Nat Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33658708 No abstract available.
Abstract
During chronic infection and cancer, a self-renewing CD8+ T cell subset maintains long-term immunity and is critical to the effectiveness of immunotherapy. These stem-like CD8+ T cells diverge from other CD8+ subsets early after chronic viral infection. However, pathways guarding stem-like CD8+ T cells against terminal exhaustion remain unclear. Here, we show that the gene encoding transcriptional repressor BACH2 is transcriptionally and epigenetically active in stem-like CD8+ T cells but not terminally exhausted cells early after infection. BACH2 overexpression enforced stem-like cell fate, whereas BACH2 deficiency impaired stem-like CD8+ T cell differentiation. Single-cell transcriptomic and epigenomic approaches revealed that BACH2 established the transcriptional and epigenetic programs of stem-like CD8+ T cells. In addition, BACH2 suppressed the molecular program driving terminal exhaustion through transcriptional repression and epigenetic silencing. Thus, our study reveals a new pathway that enforces commitment to stem-like CD8+ lineage and prevents an alternative terminally exhausted cell fate.
Figures








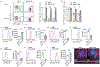
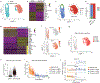




Comment in
-
BAtCHing stem-like T cells during exhaustion.Nat Immunol. 2021 Mar;22(3):274-276. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00891-8. Nat Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33627884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hashimoto M et al. CD8 T Cell Exhaustion in Chronic Infection and Cancer: Opportunities for Interventions. Annu Rev Med 69, 301–318 (2018). - PubMed
-
- McLane LM, Abdel-Hakeem MS & Wherry EJ CD8 T Cell Exhaustion During Chronic Viral Infection and Cancer. Annu Rev Immunol 37, 457–495 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Leong YA et al. CXCR5(+) follicular cytotoxic T cells control viral infection in B cell follicles. Nat Immunol 17, 1187–1196 (2016). - PubMed
Methods-only References
-
- Pircher H, Burki K, Lang R, Hengartner H & Zinkernagel RM Tolerance induction in double specific T-cell receptor transgenic mice varies with antigen. Nature 342, 559–561 (1989). - PubMed
-
- Kometani K et al. Repression of the transcription factor Bach2 contributes to predisposition of IgG1 memory B cells toward plasma cell differentiation. Immunity 39, 136–147 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Leisegang M et al. Enhanced functionality of T cell receptor-redirected T cells is defined by the transgene cassette. J Mol Med (Berl) 86, 573–583 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZIA AI001241/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI117950/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI112521/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K00 CA234842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA NS003111/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AR041106/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA210944/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA DK075149/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA NS003112/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- F99 CA234842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082630/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG056524/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI115712/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AR041167/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AR041159/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG056524/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA BC011480/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI108545/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AI001240/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI105343/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

