Application Value of Broadband 3-Dimensional Impulse Oscillometry in COPD
- PMID: 33574662
- PMCID: PMC7871874
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S285927
Application Value of Broadband 3-Dimensional Impulse Oscillometry in COPD
Abstract
Objective: To explore the correlation of respiratory resistance in stable COPD patients measured by broadband 3-dimensional impulse oscillometry (3D-IOS) and traditional pulmonary function test (PFT). To access the diagnostic value of 3D-IOS in COPD.
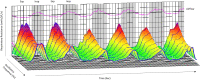
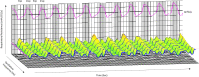
Methods: A total of 107 COPD patients and 61 healthy subjects as controls were chosen to collect and statistically analyze the data of R5, R5-R20, R20, X5 and Fres measured by broadband 3D-IOS and FEV1%pred, FVC%pred and FEV1/FVC by PFTs. The diagnostic value of broadband 3D-IOS parameters in COPD was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC). 3D-colored images used to show dynamic changes of respiratory resistance in COPD.
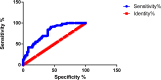
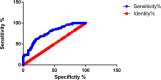
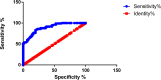
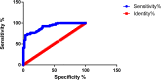
Results: The COPD group showed significant increases in R5, R20, R5-R20 and Fres, and a decrease in X5 (P<0.05). With the increase of GOLD grade, R5, R5-R20 and Fres increased whereas X5 decreased (P<0.05). Compared with FEV1%pred, FVC%pred and FEV1/FVC in the COPD group, R5, R5-R20 and Fres were negatively collated (P<0.05), whereas X5 was positively collated (P<0.01). R20 was uncorrelated with the traditional lung function parameters (P>0.05). Fres and FEV1/FVC (r=-0.467), and X5 and FEV1%pred (r=0.412) showed the strongest correlation. The AUC of R5, R5-R20, X5 and Fres was 0.7808, 0.7659, 0.8947 and 0.9095, respectively. Typical 3D-colored images of COPD displayed a green pattern in the inhalation phase and yellow-red-blue graduation in the expiration phase.
Conclusion: R5, R5-R20, X5 and Fres measured by broadband 3D-IOS can reflect the change of respiratory resistance in COPD. And they have good correlation with the traditional lung function parameters (FEV1%pred, FVC%pred, FEV1/FVC). Fres has the highest diagnostic accuracy. Comprehensive analysis of R5, R5-R20, Fres and X5 helps to determine the degree of respiratory obstruction in COPD. X5 and Fres can reflect changes in lung tissue compliance. 3D-colored images can visually show the change of respiratory resistance and reactance in COPD.
Keywords: 3-dimensional impulse oscillometry; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; pulmonary function test; respiratory resistance.
© 2021 Tang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impulse oscillometry system as an alternative diagnostic method for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Nov;96(46):e8543. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008543. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29145259 Free PMC article.
-
[The diagnostic utility of the Macao predictive values of impulse oscillometry for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in patients over 45 years old].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2016 Jan;39(1):41-6. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2016.01.012. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 26792055 Chinese.
-
Evaluation of respiratory impedance in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by an impulse oscillation system.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Nov;10(5):2694-700. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2528. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 25189185
-
Clinical Value of Impulse Oscillometry in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Respiration. 2025;104(2):100-109. doi: 10.1159/000541633. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Respiration. 2025. PMID: 39362193
-
What can we learn about COPD from impulse oscillometry?Respir Med. 2018 Jun;139:106-109. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2018.05.004. Epub 2018 May 16. Respir Med. 2018. PMID: 29857993 Review.
Cited by
-
Short-term effect of particulate matter on lung function and impulse oscillometry system (IOS) parameters of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in Beijing, China.BMC Public Health. 2023 Jul 24;23(1):1417. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16308-0. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37488590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Czajkowska-Malinowska M, Tomalak W, Radliński J. Quality of spirometry in the elderly. Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 2013;81(6):511–517. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical