Pretreatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as Prognostic Factors and Reference Markers of Treatment Options for Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma Located in the Middle and Upper Esophagus
- PMID: 33574705
- PMCID: PMC7872927
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S294344
Pretreatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as Prognostic Factors and Reference Markers of Treatment Options for Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma Located in the Middle and Upper Esophagus
Abstract
Background: Various inflammatory biomarkers, such as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), have been well authenticated to predict clinical outcomes in numerous types of cancer. The optimal treatment for patients with locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) located in the middle or upper region is still inconclusive. The aim of the study was to examine pretreatment NLR and PLR to select from radical surgery or definitive chemoradiotherapy (dCRT) for these patients. The linkage between pretreatment NLR/PLR and prognosis was also analyzed.
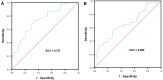
Methods: NLR and PLR were calculated in 113 locally advanced ESCC located in the middle or upper esophagus of patients who underwent radical surgery or dCRT between January 2014 and December 2019. A receiver operating characteristic curve was plotted to select the best cut-off value of NLR and PLR for predicting survival. A survival curve was plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were applied to assess predictors for survival.
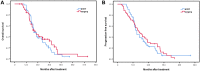
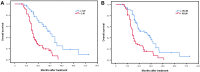
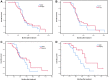
Results: NLR and PLR were associated with the extent of lymph node metastasis (NLR: P = 0.045; PLR: P = 0.002). Additionally, high PLR and recurrence with distant organ metastasis were closely related (P = 0.014), and NLR was related to the tumor stage (P = 0.043). The results of the multivariate analysis revealed that NLR (>2.07) and PLR (>183.06) were independently associated with poor prognosis. It is noteworthy that surgery was associated with a superior OS compared with dCRT in the low NLR population (P = 0.045).
Conclusion: Low pretreatment NLR patients are fit to undergo radical surgery with a substantial therapeutic benefit. Pretreatment NLR and PLR are independent predictors for patients with locally advanced ESCC located in the middle and upper esophagus who underwent radical surgery or dCRT.
Keywords: definitive chemoradiotherapy; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; prognostic factor; reference marker; surgery.
© 2021 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Study on the prognostic influencing factors of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and the predictive value of inflammatory reaction indexes on its postoperative recurrence].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2023 Feb 23;45(2):160-164. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20210326-00268. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36781237 Chinese.
-
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as Prognostic Factors in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer.Oncology. 2023;101(6):349-357. doi: 10.1159/000526450. Epub 2022 Oct 21. Oncology. 2023. PMID: 36273439
-
Can the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio be beneficial in predicting lymph node metastasis and promising prognostic markers of gastric cancer patients? Tumor maker retrospective study.Int J Surg. 2018 Aug;56:320-327. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.06.037. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Int J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29969732
-
Study on the predictive value of pretreatment peripheral blood inflammatory markers regarding immunotherapy in patients with inoperable advanced or locally advanced oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2024 Jun;59(6):722-729. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2024.2319319. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38362884
-
Pretreatment inflammatory markers predicting treatment outcomes in colorectal cancer.Ann Coloproctol. 2022 Apr;38(2):97-108. doi: 10.3393/ac.2021.01004.0143. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Ann Coloproctol. 2022. PMID: 35345306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Their Variations as a Basis for a Prediction Model in Advanced NSCLC Patients Receiving Anlotinib.Dis Markers. 2022 Mar 20;2022:5879137. doi: 10.1155/2022/5879137. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35356064 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical implications of the serum platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in the modern radiation oncology era: research update and literature review.Radiat Oncol. 2024 Aug 13;19(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13014-024-02485-8. Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39138484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pretreatment lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio as a prognostic factor and influence on dose-effect in fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for oligometastatic brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer patients.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 30;13:1216852. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1216852. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37456254 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment absolute lymphocyte count is an independent predictor for survival outcomes for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and pembrolizumab: An analysis from a prospective cohort.Thorac Cancer. 2023 Jun;14(17):1556-1566. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14898. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37089116 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Posttreatment Serum Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Distant Metastases in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Curative Radiation Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 26;15(7):1978. doi: 10.3390/cancers15071978. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046639 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

