Teaching Medical Students How to Interpret Chest X-Rays: The Design and Development of an e-Learning Resource
- PMID: 33574725
- PMCID: PMC7872944
- DOI: 10.2147/AMEP.S280941
Teaching Medical Students How to Interpret Chest X-Rays: The Design and Development of an e-Learning Resource
Abstract
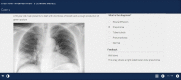
Introduction: The teaching of radiology to medical students has often been criticised for being inadequate and unstructured, with students reporting lack of confidence in assessing x-rays. In this paper, we describe how an e-learning resource, on how to interpret a chest x-ray for medical students, was designed and developed. The aim of the resource was to provide medical students with knowledge of how to interpret a chest x-ray in a systematic approach.
Methods: The technology used to design the e-learning resource was Xerte Online Toolkits. The design and development of the e-learning resource was based upon andragogical principles and followed Overbaugh's guidelines and Mayer's 12 multimedia principles. An instructional design model called ADDIE was used to help develop the resource and its content. These included cases of common conditions, a quiz and summary table at the end. The paper focuses mainly on the way in which instructional design, education and multimedia principles were used to inform the development of the resource.
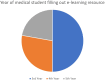
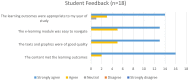
Findings: A preliminary evaluation was completed by 18 medical students from year 3-5 who completed the e-learning resource. The feedback was positive with an average rating of 9/10 and 100% of students saying they would recommend the resource to a colleague. Students commented that they liked the resource as it was easy to navigate, had good visual learning and contained good explanations with relevant content.
Conclusion and future implications: This paper demonstrates how, with the use of instructional models, educational theories and principles, an e-learning resource can be created. Preliminary evaluation showed that students were satisfied with the resource and felt it helped them acquire knowledge on how to interpret chest x-rays. This resource can be further utilized either as a standalone resource or before starting clinical placements and may prove particularly useful in the current and challenging learning environment where there is an increased need for digital resources.
Keywords: e-learning; educational principles; instructional design; learning outcomes; medical students; radiology.
© 2021 Sait and Tombs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Teaching Medical Students About Kawasaki Disease: The Development and Evaluation of a Digital Educational Resource.Adv Med Educ Pract. 2023 May 24;14:515-522. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S399178. eCollection 2023. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2023. PMID: 37251429 Free PMC article.
-
Teaching Medical Students About Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): The Design And Development Of An E-Learning Resource.Adv Med Educ Pract. 2019 Nov 20;10:987-997. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S220390. eCollection 2019. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2019. PMID: 31819698 Free PMC article.
-
Applying multimedia design principles enhances learning in medical education.Med Educ. 2011 Aug;45(8):818-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.2011.03988.x. Med Educ. 2011. PMID: 21752078
-
MEDICOL: online learning in medicine and dentistry.Acad Med. 2002 Sep;77(9):926-7. doi: 10.1097/00001888-200209000-00028. Acad Med. 2002. PMID: 12228095 Review.
-
Otolaryngology--head and neck surgery in undergraduate medical education: advances and innovations.Laryngoscope. 2015 Feb;125 Suppl 2:S1-14. doi: 10.1002/lary.24875. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Laryngoscope. 2015. PMID: 25124523 Review.
Cited by
-
Anatomy-Guided Weakly-Supervised Abnormality Localization in Chest X-rays.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2022 Sep;13435:658-668. Epub 2022 Sep 16. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2022. PMID: 38952749 Free PMC article.
-
An Evaluation of the Design of Multimedia Patient Education Materials in Musculoskeletal Health Care: Systematic Review.JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2024 Oct 15;11:e48154. doi: 10.2196/48154. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2024. PMID: 39162239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Designing multimedia patient education materials for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A protocol for a feasibility randomized controlled trial of patient education videos.PLoS One. 2024 May 23;19(5):e0297394. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297394. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38781168 Free PMC article.
-
Chest X-Ray Assessment is Incomplete without the Lateral View [Letter].Adv Med Educ Pract. 2021 Mar 4;12:245-246. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S306149. eCollection 2021. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2021. PMID: 33692646 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Blending electronic techniques with traditional teaching methods to enhance chest X-ray interpretation in medical students.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 6;20(8):e0328159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328159. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40768399 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Council GM. Tomorrow’s Doctors: Outcomes and Standards for Undergraduate Medical Education. Manchester, UK: General Medical Council; 2009.
-
- Royal College of Radiologists. Undergraduate radiology curriculum (2nd ed). 2017. Available from: https://www.rcr.ac.uk/sites/default/files/documents/undergraduate_radiol.... Accessed November22, 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

