Safety and Efficacy of Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Inhibitors for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies and Solid Tumors: A Systematic Study of Clinical Trials
- PMID: 33574760
- PMCID: PMC7870522
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.621093
Safety and Efficacy of Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Inhibitors for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies and Solid Tumors: A Systematic Study of Clinical Trials
Abstract
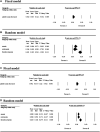
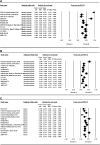
Background: The upregulated expression of BET proteins is closely associated with the occurrence and development of hematological malignancies and solid tumors. Several BET inhibitors have been developed, and some have been in phase I/II of clinical trials. Here, the safety, efficacy, and pharmacodynamics of ten BET inhibitors currently in clinical trials were evaluated. Methods: We retrieved and reviewed published reports on the clinical trials of twelve BET inhibitors including AZD5153, ABBV-075, BMS-986158, CPI-0610, GSK525762, OTX-015, PLX51107, INCB054329, INCB057643, FT-1101, CC-90010, and ODM-207 for patients with hematological malignancies and solid tumors and summarized their published target genes. Results: In the monotherapy of BET inhibitors, the most common and severe (grade ≥3) hematological adverse events (AEs) are thrombocytopenia, anemia, and neutropenia. The most common non-hematological syndromes are diarrhea, nausea, fatigue, dysgeusia, and decreased appetite, while the most severe AE is pneumonia. Additionally, T max of these BET inhibitors was between 0.5-6 h, but the range for T 1/2 varied significantly. According to published data, the rates of SD, PD, CR and PR were 27.4%, 37.6%, 3.5%, and 5.7%, respectively, which is not very satisfactory. In addition to BRD4, oncogene MYC is another common target gene of these BET inhibitors. Ninety-seven signaling pathways may be regulated by BET inhibitors. Conclusion: All BET inhibitors reviewed in our study exhibited exposure-dependent thrombocytopenia, which may limit their clinical application. Moreover, further efforts are necessary to explore the optimal dosing schemes and combinations to maximize the efficacy of BET inhibitors.
Keywords: bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitor; efficacy; hematological malignancy; safety; solid tumor.
Copyright © 2021 Sun, Han, Wang, Li, Sun and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Development of 2 Bromodomain and Extraterminal Inhibitors With Distinct Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Profiles for the Treatment of Advanced Malignancies.Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Mar 15;26(6):1247-1257. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-4071. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31527168 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of FLT3 inhibitors in monotherapy of hematological and solid malignancies: a systemic analysis of clinical trials.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 17;15:1294668. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1294668. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38828446 Free PMC article.
-
BET inhibitors: a novel epigenetic approach.Ann Oncol. 2017 Aug 1;28(8):1776-1787. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx157. Ann Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28838216 Review.
-
Bromodomain and extra-terminal inhibitors-A consensus prioritisation after the Paediatric Strategy Forum for medicinal product development of epigenetic modifiers in children-ACCELERATE.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Mar;146:115-124. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.01.018. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33601323 Review.
-
AZD5153: A Novel Bivalent BET Bromodomain Inhibitor Highly Active against Hematologic Malignancies.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Nov;15(11):2563-2574. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0141. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27573426
Cited by
-
Multiomic Characterization and Molecular Profiling of Nuclear Protein in Testis Carcinoma.JCO Precis Oncol. 2024 Oct;8:e2400334. doi: 10.1200/PO.24.00334. Epub 2024 Oct 24. JCO Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39447095 Free PMC article.
-
The role of protein acetylation in carcinogenesis and targeted drug discovery.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 12;13:972312. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.972312. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36171897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BRD4 Inhibition as a Strategy to Prolong the Response to Standard of Care in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;15(16):4066. doi: 10.3390/cancers15164066. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627092 Free PMC article.
-
BET Bromodomain Inhibitors: Novel Design Strategies and Therapeutic Applications.Molecules. 2023 Mar 29;28(7):3043. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073043. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relevance of BET Family Proteins in SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Biomolecules. 2021 Jul 30;11(8):1126. doi: 10.3390/biom11081126. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amorim S., Stathis A., Gleeson M., Iyengar S., Magarotto V., Leleu X., et al. (2016). Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 in patients with lymphoma or multiple myeloma: a dose-escalation, open-label, pharmacokinetic, phase 1 study. Lancet Haematol. 3 (4), e196–e204. 10.1016/S2352-3026(16)00021-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

