Kiwi Root Extract Inhibits the Development of Endometriosis in Mice by Downregulating Inflammatory Factors
- PMID: 33574880
- PMCID: PMC7857878
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/4536132
Kiwi Root Extract Inhibits the Development of Endometriosis in Mice by Downregulating Inflammatory Factors
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether the kiwi root extract inhibits the development of endometriosis in mice by suppressing inflammatory factors.
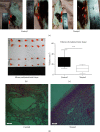
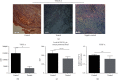
Materials and methods: The mouse model of endometriosis was induced by surgery after which the mice were continuously injected with the drug for 14 days. On the 14th day, the mice were sacrificed, and the peritoneal fluid was obtained for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Endometrial ectopic tissue was weighed and analyzed by tissue immunochemistry, RT-PCR, western blotting, and gelatin zymography experiment.
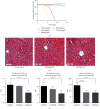
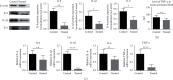
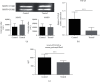
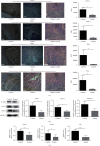
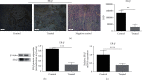
Results: Kiwi root extract significantly reduced endometriotic lesion volume and downregulated the proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and TNF-α, as well as the angiogenic factor VEGF-A. It also inhibited the mRNA and protein expression of COX-1 and COX-2, IL-6, TGF-β1, EP2 receptor, and ER-β in endometriotic lesions but did not affect the expression of MMP-9 and MMP-2.
Conclusions: Kiwi root extract could significantly inhibit the growth of surgery-induced endometriosis in mice. Our results suggest that the kiwi root extract may inhibit the development and progression of ectopic endometrium through disruption of neovascularization and reducing inflammation, which may be beneficial in treating this common gynecological disease.
Copyright © 2021 Tingting Liao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yu J., Chen L. H., Zhang B., Zheng Q. M. The modulation of endometriosis by lncrna Malat1 via nf-kappab/inos. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2019;23(10):4073–4080. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

