In vivo detection of vertical root fractures in endodontically treated teeth: Accuracy of cone-beam computed tomography and assessment of potential predictor variables
- PMID: 33574996
- PMCID: PMC7864364
- DOI: 10.4317/jced.57471
In vivo detection of vertical root fractures in endodontically treated teeth: Accuracy of cone-beam computed tomography and assessment of potential predictor variables
Abstract
Background: This study aimed: (a) to determine the diagnostic performance of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) for detection of vertical root fractures (VRFs); (b) to evaluate the predictive value of diagnostic criteria regarding the definition of VRFs; and (c) to examine the robustness of the association of patient-, tooth-, and treatment-related variables with VRFs.
Material and methods: 130 root-filled teeth with signs/symptoms of VRFs underwent clinical and CBCT assessments. Definite diagnosis of VRF was confirmed by endodontic microsurgical (EMS) exploration. Determination of diagnostic performance of CBCT was based on standard algorithms derived from two-way contingency table analysis. Predictive value of diagnostic criteria and the association between predictor variables with VRFs were analyzed using logistic regression models.
Results: VRFs were detected during EMS in 50% of the teeth. Based on the finding of fracture lines on CBCT scans, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 86.2%, 13.8%, and 50%, respectively. Teeth having more than three diagnostic criteria present had significant higher odds for VRF diagnosis. After logistic regression analysis, parafunctional habits, one-canal roots, excessive root canal enlargement, and absence of intra-radicular posts remained as robust predictor variables of VRFs.
Conclusions: Although the sensitivity of CBCT for VRFs detection is high, the risk of false-positive results related to its low specificity makes that all suspected cases must be confirmed by surgical exploration. VRFs cannot be reliably diagnosed by isolated clinical signs/symptoms; instead those teeth possessing more than three diagnostic criteria might be considered practically pathognomonic. The parafunctional habits, one-canal roots, excessive root canal enlargement, and the absence of intra-radicular posts may act strongly/independently for the occurrence of VRFs in endodontically treated teeth. Key words:Cone-beam computed tomography, diagnostic accuracy, diagnostic surgery, predictor variables, root canal treatment, vertical root fracture.
Copyright: © 2021 Medicina Oral S.L.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest None declared.
Figures
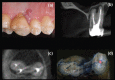
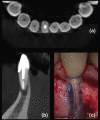
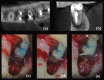
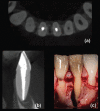
References
-
- Dutra KL, Pachêco-Pereira C, Bortoluzzi EA, Flores-Mir C, Lagravère MO, Corrêa M. Influence of intracanal materials in vertical root fracture pathway detection with cone-beam computed tomography. J Endod. 2017;43:1170–5. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Wang T, Cao Y, Wang C, Tan B, Tang X. In vivo detection of subtle vertical root fracture in endodontically treated teeth by cone-beam computed tomography. J Endod. 2019;45:856–62. - PubMed
-
- Kamburoğlu K, Murat S, Yüksel SP, Cebeci AR, Horasan S. Detection of vertical root fracture using cone-beam computerized tomography: an in vitro assessment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109:e74–81. - PubMed
-
- Rivera EM, Walton RE. Longitudinal tooth fractures: findings that contribute to complex endodontic diagnoses. Endod Topics. 2009;16:82–111.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
