The Predictive Value of Interleukin-6 and Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Severe and Extremely Severe Oral and Maxillofacial Space Infections
- PMID: 33575324
- PMCID: PMC7861909
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2615059
The Predictive Value of Interleukin-6 and Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Severe and Extremely Severe Oral and Maxillofacial Space Infections
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the correlation between clinical manifestation and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, C-reactive protein (CRP), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the patients with severe and extremely severe oral and maxillofacial space infection (OMSI).
Methods: In this retrospective study, we included 18 patients with severe and extremely severe OMSI from November 2012 to October 2018. Pearson or Spearman correlation coefficients were calculated to measure the association between the number of complications and locations and the number and percentage of lymphocyte, leukocyte, neutrophil, eosinophil, basophil, monocyte, CRP, and IL-6. A multivariable regression model was used to predict the number of complications and locations from these measures.
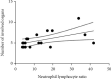
Results: IL-6 was positively correlated with neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (r s = 0.773, P = 0.005), percentage of neutrophil (r s = 0.927, P = 0.001), and the number of neutrophil (r s = 0.627, P = 0.039). It was negatively correlated with percentage of monocyte (r s = -0.773, P = 0.005). CRP was positively correlated with neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (r s = 0.556, P = 0.020) and percentage of neutrophil (r s = 0.515, P = 0.035). It was negatively correlated with the number of lymphocyte (r s = -0.517, P = 0.017), percentage of lymphocyte (r s = -0.578, P = 0.015), number of eosinophil (r s = -0.560, P = 0.020), percentage of eosinophil (r s = -0.504, P = 0.039), number of basophil (r s = -0.504, P = 0.039), and percentage of basophil (r s = -0.548, P = 0.023). The number of the involved organs was positively correlated with neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (r s = 0.511, P = 0.030). The number of complications was positively correlated with the percentage of neutrophils (r = 0.738, P = 0.001), the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (r = 0.576, P = 0.012), IL-6 (r s = 0.907, P = 0.001), and CRP (r s = 0.599, P = 0.011). Multivariable regression analysis showed that the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (β = 0.080) was a significant predictor of the number of the involved organs and the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (β = 0.099). In addition, IL-6 (β = 0.002) was a significant predictor of the number of complications.
Conclusions: The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and IL-6 contributed to the assessment of general condition in severe and profound OMSI patients. These parameters can be used as predictors to evaluate the severity of OMSI.
Copyright © 2021 Li Xiaojie et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
When is surgical intervention needed in oral and maxillofacial space infection patients? A retrospective case control study in 46 patients.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Aug 22;24(1):973. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04737-1. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39169339 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-neutrophil ratio, and neutrophil-to-monocyte ratio in lupus nephritis.Lupus. 2020 Aug;29(9):1031-1039. doi: 10.1177/0961203320929753. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Lupus. 2020. PMID: 32501169
-
Comparisons of neutrophil-, monocyte-, eosinophil-, and basophil- lymphocyte ratios among various systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases.APMIS. 2017 Oct;125(10):863-871. doi: 10.1111/apm.12722. Epub 2017 Aug 2. APMIS. 2017. PMID: 28766758
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, a critical predictor for assessment of disease severity in patients with COVID-19.Int J Lab Hematol. 2021 Apr;43(2):329-335. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13374. Epub 2020 Oct 25. Int J Lab Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33099889
-
Correlation analysis between disease severity and inflammation-related parameters in patients with COVID-19: a retrospective study.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Dec 21;20(1):963. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05681-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33349241 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
When is surgical intervention needed in oral and maxillofacial space infection patients? A retrospective case control study in 46 patients.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Aug 22;24(1):973. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04737-1. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39169339 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the prognostic value of CRP and neutrophil lymphocyte ratio in patients hospitalized for deep neck infection.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Nov-Dec;90(6):101492. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101492. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 39205364 Free PMC article.
-
Oral and Maxillofacial Infections-A Bacterial and Clinical Cross-Section.J Clin Med. 2022 May 12;11(10):2731. doi: 10.3390/jcm11102731. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35628858 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in odontogenic infection: a systematic review.Head Face Med. 2024 Mar 28;20(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13005-024-00421-5. Head Face Med. 2024. PMID: 38539204 Free PMC article.
-
Negative pressure sealing drainage technology combined with adequate irrigation for oral and maxillofacial space infection can improve serum inflammatory factor levels.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Nov 15;15(11):6605-6612. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38074802 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous