BRAKER2: automatic eukaryotic genome annotation with GeneMark-EP+ and AUGUSTUS supported by a protein database
- PMID: 33575650
- PMCID: PMC7787252
- DOI: 10.1093/nargab/lqaa108
BRAKER2: automatic eukaryotic genome annotation with GeneMark-EP+ and AUGUSTUS supported by a protein database
Abstract
The task of eukaryotic genome annotation remains challenging. Only a few genomes could serve as standards of annotation achieved through a tremendous investment of human curation efforts. Still, the correctness of all alternative isoforms, even in the best-annotated genomes, could be a good subject for further investigation. The new BRAKER2 pipeline generates and integrates external protein support into the iterative process of training and gene prediction by GeneMark-EP+ and AUGUSTUS. BRAKER2 continues the line started by BRAKER1 where self-training GeneMark-ET and AUGUSTUS made gene predictions supported by transcriptomic data. Among the challenges addressed by the new pipeline was a generation of reliable hints to protein-coding exon boundaries from likely homologous but evolutionarily distant proteins. In comparison with other pipelines for eukaryotic genome annotation, BRAKER2 is fully automatic. It is favorably compared under equal conditions with other pipelines, e.g. MAKER2, in terms of accuracy and performance. Development of BRAKER2 should facilitate solving the task of harmonization of annotation of protein-coding genes in genomes of different eukaryotic species. However, we fully understand that several more innovations are needed in transcriptomic and proteomic technologies as well as in algorithmic development to reach the goal of highly accurate annotation of eukaryotic genomes.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of NAR Genomics and Bioinformatics.
Figures
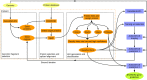

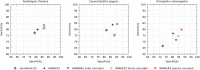
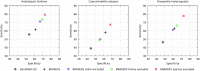
References
-
- Zheng H., Zhang W., Zhang L., Zhang Z., Li J., Lu G., Zhu Y., Wang Y., Huang Y., Liu J. et al. The genome of the hydatid tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus. Nat. Genet. 2013; 45:1168–1175. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

