Arthritis in systemic lupus erythematosus is characterized by local IL-17A and IL-6 expression in synovial fluid
- PMID: 33576004
- PMCID: PMC8209560
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13585
Arthritis in systemic lupus erythematosus is characterized by local IL-17A and IL-6 expression in synovial fluid
Abstract
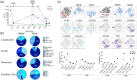
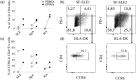
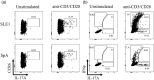
Arthritis is a common clinical feature of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and is usually non-erosive, as opposed to rheumatoid arthritis (RA). While RA synovial pathology has been extensively studied, little is known about the pathophysiology of lupus arthritis. Here, we aimed to explore the cytokine and cellular compartments in synovial fluids of SLE patients with arthritic manifestations. Acellular synovial fluid and paired serum samples from SLE patients (n = 17) were analyzed with cytokine bead array for T helper-associated cytokines. From two SLE patients, synovial fluid mononuclear cells (SFMC) could also be captured and were analyzed by multiparameter flow cytometry to dissect T cell, B cell, monocyte and dendritic cell phenotypes. SLE-derived SFMC were further stimulated in vitro to measure their capacity for producing interferon (IFN)-γ and interleukin (IL)-17A. All patients fulfilled the ACR 1982 classification criteria for SLE. Clinical records were reviewed to exclude the presence of co-morbidities such as osteoarthritis or overlap with RA. IL-17A and IL-6 levels were high in SLE synovial fluid. A clear subset of the synovial CD4+ T cells expressed CCR6+ , a marker associated with T helper type 17 (Th17) cells. IL-17A-production was validated among CD4+ CCR6+ T cells following in-vitro stimulation. Furthermore, a strong IFN-γ production was observed in both CD4+ and CD8+ cells. Our study shows high IL-17A and IL-6 levels in synovial fluids of patients with lupus arthritis. The Th17 pathway has been implicated in several aspects of SLE disease pathogenesis and our data also point to Th17 involvement for lupus arthritis.
Keywords: T cells; arthritis; cytokines; synovial fluid; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical & Experimental Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Society for Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Ball EM, Bell AL. Lupus arthritis – do we have a clinically useful classification? Rheumatology 2012; 51:771–9. - PubMed
-
- Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1982; 25:1271–7. - PubMed
-
- Zayat AS, Mahmoud K, Md Yusof MY et al. Defining inflammatory musculoskeletal manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 2019; 58:304–12. - PubMed
-
- Tani C, D’Aniello D, Possemato N et al. MRI pattern of arthritis in systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparative study with rheumatoid arthritis and healthy subjects. Skeletal Radiol 2015; 44:261–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

