Procyanidin B2 inhibits lipopolysaccharide‑induced apoptosis by suppressing the Bcl‑2/Bax and NF‑κB signalling pathways in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMID: 33576443
- PMCID: PMC7893691
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.11906
Procyanidin B2 inhibits lipopolysaccharide‑induced apoptosis by suppressing the Bcl‑2/Bax and NF‑κB signalling pathways in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Abstract
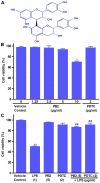
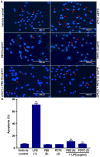
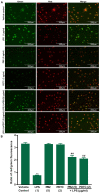
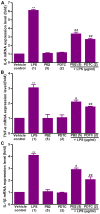
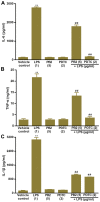
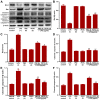
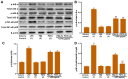
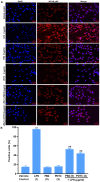
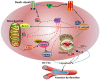
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) serve a critical role in maintaining normal vascular function. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which is released from pathogenic bacteria in the blood, induces HUVEC apoptosis and injury to cause vascular dysfunction and infectious vascular diseases. Procyanidin B2 (PB2) possesses numerous functions, including antioxidant, antitumor, anti‑inflammatory and antiapoptosis effects, but the molecular mechanism is not completely understood. The present study investigated the effects of PB2 on LPS‑induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in HUVECs, as well as the underlying mechanisms. The effects of PB2 on LPS‑mediated alterations to cytotoxicity, mitochondrial membrane potential, apoptosis were assessed by performing Cell Counting Kit‑8, JC‑1 fluorescence, Hoechst 33258 staining assays, respectively. IL‑1β, IL‑6 and TNF‑α mRNA expression and protein levels were measured by performing reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR and ELISAs, respectively. Bcl‑2, Bax, cleaved caspase‑3, cleaved caspase‑7, cleaved caspase‑9, phosphorylated (p)‑IκB‑α, p‑IκB‑β, p‑NF‑κB‑p65 and total NF‑κB p65 protein expression levels were determined via western blotting. NF‑κB p65 nuclear translocation was assessed via immunofluorescence. PB2 pretreatment markedly attenuated LPS‑induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in HUVECs. PB2 also significantly downregulated the expression levels of IL‑1β, IL‑6, TNF‑α, Bax, cleaved caspase‑3, cleaved caspase‑7, cleaved caspase‑9 and p‑NF‑κB‑p65, but upregulated the expression levels of Bcl‑2, p‑IκB‑α and p‑IκB‑β in LPS‑induced HUVECs. Moreover, PB2 markedly inhibited LPS‑induced NF‑κB p65 nuclear translocation in HUVECs. The results suggested that the potential molecular mechanism underlying PB2 was associated with the Bax/Bcl‑2 and NF‑κB signalling pathways. Therefore, PB2 may serve as a useful therapeutic for infectious vascular diseases.
Keywords: PB2; LPS; apoptosis; NF‑κB; cytokine; HUVECs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N‑acetyl cysteine inhibits lipopolysaccharide‑induced apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells via the p38MAPK signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Sep;20(3):2945-2953. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10526. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31524245
-
Procyanidin B2 alleviates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced cell injury, inflammation, monocyte chemotaxis, and oxidative stress by inhibiting the nuclear factor kappa-B pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Apr 29;24(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03858-3. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38679696 Free PMC article.
-
Gas6 attenuates lipopolysaccharide‑induced TNF‑α expression and apoptosis in H9C2 cells through NF‑κB and MAPK inhibition via the Axl/PI3K/Akt pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Sep;44(3):982-994. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4275. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31524235 Free PMC article.
-
Puerarin prevents vascular endothelial injury through suppression of NF-κB activation in LPS-challenged human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Aug;104:261-267. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.038. Epub 2018 May 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29775893
-
Isoquercitrin protects HUVECs against high glucose‑induced apoptosis through regulating p53 proteasomal degradation.Int J Mol Med. 2021 Jul;48(1):122. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4955. Epub 2021 May 13. Int J Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33982778 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of miR-412-5p-loaded exosomes in H9c2 cardiomyocytes via the MAPK pathway.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(6):755-760. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2024.75590.16365. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38645496 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemicals as potential target on thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Feb;31(1):207-220. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01130-8. Epub 2023 Jan 7. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36609715 Review.
-
Role of Plant-Derived Compounds in the Molecular Pathways Related to Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 28;24(5):4666. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054666. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of procyanidins in repairing cartilage injury after anterior cruciate ligament tear.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 18;10(4):e26070. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26070. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38420419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Amnesia-like Effect of Pinus densiflora Extract by Improving Apoptosis and Neuroinflammation on Trimethyltin-Induced ICR Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 14;24(18):14084. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814084. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yao Z, Mates JM, Cheplowitz AM, Hammer LP, Maiseyeu A, Phillips GS, Wewers MD, Rajaram MV, Robinson JM, Anderson CL, Ganesan LP. Blood-borne lipopolysaccharide is rapidly eliminated by liver sinusoidal endothelial cells via high-density lipoprotein. J Immunol. 2016;197:2390–2399. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600702. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

