Involvement of non‑coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (Review)
- PMID: 33576444
- PMCID: PMC7895537
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4875
Involvement of non‑coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (Review)
Abstract
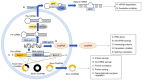
Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI) may cause myocardial stunning, reperfusion arrhythmia, no‑reflow phenomenon and lethal reperfusion injury, which has a significant effect on the prognosis of patients undergoing thrombolytic agent therapy and percutaneous coronary intervention. Increasing evidence suggests that apoptosis, innate inflammation, oxidative stress, calcium overload and autophagy are involved in the pathogenesis of MIRI. Recent advancements in RNA sequencing technologies and genome‑wide analyses led to the finding of small non‑coding RNAs (ncRNAs). ncRNAs modulate cellular processes such as signal transduction, transcription, chromatin remodeling and post‑transcriptional modification. The effects of ncRNAs on cellular biology is more considerable than initially expected, and thus ncRNAs have gained increasing attention and focus in modern medical research. There are several types of ncRNAs, such as microRNAs (miRNAs), long non‑coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs), which have been shown to regulate gene expression at the transcription, post‑transcription and epigenetic levels. Dysregulation of ncRNAs, including miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs, may participate in the molecular mechanisms of MIRI. The present review summarizes the characteristics and biological roles of miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs, with particular emphasis on their role in MIRI, which show the novel complexity of ischemic hearts and may offer valuable insights into the pathogenesis of MIRI.
Keywords: myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury; microRNA; long non‑coding RNA; circular RNA; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Das SR, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:e56–e528. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

