Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Liver Transplantation and Underlying Diseases: New Insights and Therapeutics
- PMID: 33577251
- PMCID: PMC9005104
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003691
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Liver Transplantation and Underlying Diseases: New Insights and Therapeutics
Abstract
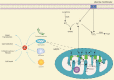
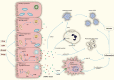
Mitochondria are essential organelles for cellular energy and metabolism. Like with any organ, the liver highly depends on the function of these cellular powerhouses. Hepatotoxic insults often lead to an impairment of mitochondrial activity and an increase in oxidative stress, thereby compromising the metabolic and synthetic functions. Mitochondria play a critical role in ATP synthesis and the production or scavenging of free radicals. Mitochondria orchestrate many cellular signaling pathways involved in the regulation of cell death, metabolism, cell division, and progenitor cell differentiation. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress are closely associated with ischemia-reperfusion injury during organ transplantation and with different liver diseases, including cholestasis, steatosis, viral hepatitis, and drug-induced liver injury. To develop novel mitochondria-targeting therapies or interventions, a better understanding of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in hepatic pathogenesis is very much needed. Therapies targeting mitochondria impairment and oxidative imbalance in liver diseases have been extensively studied in preclinical and clinical research. In this review, we provide an overview of how oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction affect liver diseases and liver transplantation. Furthermore, we summarize recent developments of antioxidant and mitochondria-targeted interventions.
Copyright © 2021 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytidine-5'-Diphosphocholine Protects the Liver From Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Preserving Mitochondrial Function and Reducing Oxidative Stress.Liver Transpl. 2018 Aug;24(8):1070-1083. doi: 10.1002/lt.25179. Liver Transpl. 2018. PMID: 29679463
-
IDH2 deficiency increases the liver susceptibility to ischemia-reperfusion injury via increased mitochondrial oxidative injury.Redox Biol. 2018 Apr;14:142-153. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 28938192 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into mitochondrial targeting strategies in liver transplantation.Int J Med Sci. 2018 Jan 8;15(3):248-256. doi: 10.7150/ijms.22891. eCollection 2018. Int J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29483816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
The Role of Mitochondria in Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: From Aspects of Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Fission, Mitochondrial Membrane Permeable Transport Pore Formation, Mitophagy, and Mitochondria-Related Protective Measures.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jul 5;2021:6670579. doi: 10.1155/2021/6670579. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34285766 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial respiration during normothermic liver machine perfusion predicts clinical outcome.EBioMedicine. 2022 Nov;85:104311. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104311. Epub 2022 Oct 29. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 36374770 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The interaction between COX-2 and endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 15;52(1):710. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10814-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40663274
-
Hepatoprotective effects of Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb. extract via free radical scavenger, inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation mechanisms in acetaminophen-induced liver injury.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(8):1100-1106. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.82500.17833. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40584441 Free PMC article.
-
HAX1 maintains the glioma progression in hypoxia through promoting mitochondrial fission.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Dec;25(24):11170-11184. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17038. Epub 2021 Nov 10. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34755451 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Exosomes Mediate Neurodegeneration Following Hepatic Ischemia-reperfusion Through Inducing Microglial Pyroptosis in the Developing Hippocampus.Transplantation. 2023 Nov 1;107(11):2364-2376. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000004664. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Transplantation. 2023. PMID: 37291725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayala-Peña S, Torres-Ramos CA.Preedy VR, ed. Oxidative stress, aging and mitochondrial dysfunction in liver pathology. In: Aging 2014Academic Press; 39–48.
-
- Mansouri A, Gattolliat CH, Asselah T. Mitochondrial dysfunction and signaling in chronic liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:629–647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

