Measurement properties of the one-minute sit-to-stand test in children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis: A multicenter randomized cross-over trial
- PMID: 33577586
- PMCID: PMC7880481
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246781
Measurement properties of the one-minute sit-to-stand test in children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis: A multicenter randomized cross-over trial
Abstract
Background: Functional exercise capacity assessment is recommended in children with cystic fibrosis (CF). The six-minute walk test (6MWT) is a valid evaluation of exercise capacity but can be technically complex. Inversely, the sit-to-stand test (STST) is a simple method to evaluate exercise capacity, and is validated in healthy children and adults with CF. This study aimed to evaluate STST measurement properties in children and adolescents with CF.
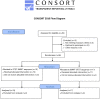
Methods: In this multicenter study, children with CF (6 to 18 years) performed two iterations of both the STST and the 6MWT in a randomized order. Criterion validity was determined by assessing correlations between STST repetitions and 6MWT distance (6MWD). Intra-rater reliability, test-retest repeatability, mean bias and limits of agreement were also assessed. Relationships with other outcomes (i.e. respiratory and quadriceps muscle strength) and cardio-respiratory responses were analysed for both tests.
Results: Thirty-six children with CF were included (mean age 12.0 ±3.5 years and FEV1 95.8 ±25.0%). On average, 39.6 ±10.5 repetitions were performed during the STST and mean 6MWD was 596.0 ±102.6 meters. STST number of repetitions was significantly correlated with 6MWD (r = 0.48; p<0.01). Both tests had very good intra-rater reliability (ICCSTST = 0.91 (95%CI 0.76-0.96) and ICC6MWT = 0.94 (95%CI 0.85-0.97)), and a significant test-retest learning effect. The number of STST repetitions was not correlated with quadriceps or respiratory muscle strength test, and the STST induced fewer cardio-respiratory responses than the 6MWT.
Conclusions: The STST is an easy-to-use functional test with moderate criterion validity when compared to the 6MWT in children with CF, probably because both tests measure different components of functional exercise capacity. The STST is useful when the 6MWT is unfeasible, however further investigations are required to explore the clinical implications of STST results in children with CF.
Clinical trial registration: NCT03069625.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests. Prof. Bouchra Lamia reports expertise activities from Novartis, Chiesi, and from Astra Zeneca, non-financial support from Philips Respironics, grants from Lowenstein, grants from Bayer, and expertise activies from Elivie, all outside the submitted work. Mr. Tristan Bonnevie reports grants from Fisher & Paykel, outside the submitted work. All the other authors have no competing interests to declare. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

