SARS-CoV-2 decontamination of skin with disinfectants active during and after application
- PMID: 33577834
- PMCID: PMC7873612
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhin.2021.02.004
SARS-CoV-2 decontamination of skin with disinfectants active during and after application
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic has resulted in high levels of exposure of medical workers to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Hand decontamination is one of the actions recommended to reduce the risk of infection.
Aim: Two disinfectants - BIAKŌS antimicrobial skin and wound cleanser (AWC) and AWC2 (Sanara MedTech, Fort Worth, TX, USA) - were tested to determine whether they can inactivate SARS-CoV-2 upon contact or as a coating applied before contact with the virus.
Methods: The ability of AWC and AWC2 to inactivate SARS-CoV-2 was tested in liquid and dried form on plastic surfaces and porcine skin.
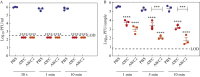
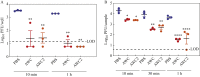
Findings: AWC and AWC2 were effective in reducing the infectious titre of SARS-CoV-2 in liquid form during application and in dried form 4 h after application. Virus on skin was reduced up to 2 log10-fold and 3.5 log10-fold after treatment with AWC and AWC2, respectively.
Conclusion: Application of AWC and AWC2 to skin reduces the level of SARS-CoV-2 and the risk of infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; Disinfection; SARS-CoV-2; Skin.
Copyright © 2021 The Healthcare Infection Society. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Smit H.A., Burdorf A., Coenraads P.J. Prevalence of hand dermatitis in different occupations. Int J Epidemiol. 1993;22:288–293. - PubMed
-
- O'Connell K.A., Enos C.W., Prodanovic E. Handwashing-induced dermatitis during the COVID-19 pandemic. Am Fam Physician. 2020;102:327–328. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert P., Moore L.E. Cationic antiseptics: diversity of action under a common epithet. J Appl Microbiol. 2005;99:703–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

