Gender-specific association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus among a middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: An observational study
- PMID: 33578624
- PMCID: PMC10545277
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024743
Gender-specific association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus among a middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: An observational study
Abstract
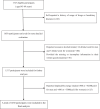
Limited data are available regarding the association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in China. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the gender-specific association between NAFLD and T2DM risk in a middle-aged and elderly Chinese population.This cross-sectional study was carried out in a group of 1492 Chinese adults (60.30% males) aged between 45 and 69 years old, in Hangzhou city, Zhejiang province who were attending their annual health check-up from June 2015 to December 2016 in the Medical Center for Physical Examination, Zhejiang Hospital. Face-to-face interviews were conducted using a written questionnaire. NAFLD was divided into none, mild, moderate/severe based on ultrasound examination. Logistic regression analyses were employed to determine the relationship between NAFLD and the risk of T2DM, with adjustment of potential confounding variables.Of the 1492 participants, 163 (10.92%) were diagnosed with T2DM. Educational level, smoking, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), waist-hip ratio (WHR), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), fasting glucose (FG), triglycerides (TG), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), asparagine aminotransferase (AST)and the prevalence of T2DM were significantly higher in males than in females (P < .05). Besides, females had significantly higher levels of high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) (1.51 ± 0.37 vs 1.29 ± 0.42, P < .001) than males. Pearson bivariate correlation analysis indicated that FG was positively associated with weight, BMI, WC, WHR, SBP, DBP, TG, TC, ALT and AST in both males and females (P < .05). Besides, FG was inversely associated with HDL-C in females (P < .001). After adjusting for confounding variables, NAFLD was positively associated with the risk of T2DM, and the effect of NAFLD on T2DM was stronger in males (OR = 2.442, 95%CI: 1.003-3.757) than in females (OR = 1.814, 95%CI: 1.011-3.257).Our data showed that NAFLD was significantly associated with the risk of T2DM in middle-aged and elderly males than in females. Further prospective cohort studies are needed to determine the causal effect of NAFLD on T2DM.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gender difference on the relationship between hyperuricemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among Chinese: An observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Sep;96(39):e8164. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008164. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28953666 Free PMC article.
-
Gender impacts on the correlations between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hypertension in a Chinese population aged 45-60 y.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2016;38(7):639-643. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2016.1182181. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27680771
-
[Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease increases the incidence rate of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cohort study based on a rural town elderly population of southern Jiangsu].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2021 Sep 20;29(9):867-872. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20200429-00223. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34638206 Chinese.
-
Association between fatty liver disease and risk of microvascular complications in Type-2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pak J Med Sci. 2025 Mar;41(3):902-909. doi: 10.12669/pjms.41.3.11362. Pak J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40103889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type 2 diabetes originated from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Life Metab. 2023 Feb 21;2(1):load007. doi: 10.1093/lifemeta/load007. eCollection 2023 Feb. Life Metab. 2023. PMID: 39872510 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Sierra Leone, 1997-2022: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2023 May 22;109(1):105-114. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.22-0711. Print 2023 Jul 5. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2023. PMID: 37217165 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-The Chicken or the Egg Dilemma.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 4;11(4):1097. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041097. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and liver cirrhosis in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Diabetes. 2024 May;16(5):e13564. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13564. J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38664879 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Features of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in the Non-Lean Population.Obes Facts. 2023;16(5):427-434. doi: 10.1159/000530845. Epub 2023 May 22. Obes Facts. 2023. PMID: 37231905 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of elevated liver enzymes and its relationship with type 2 diabetes mellitus in North Indian adults.Metabol Open. 2021 Sep 24;12:100130. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100130. eCollection 2021 Dec. Metabol Open. 2021. PMID: 34622192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016;64:73–84. - PubMed
-
- Younossi ZM, Blissett D, Blissett R, et al. The economic and clinical burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States and Europe. Hepatology 2016;64:1577–86. - PubMed
-
- Anstee QM, Targher G, Day CP. Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;10:330–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous