Rate of neuropathic progression in hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy and other peripheral neuropathies: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33579211
- PMCID: PMC7879641
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-021-02094-y
Rate of neuropathic progression in hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy and other peripheral neuropathies: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: We aimed to compare neuropathic progression rate between hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy (ATTRv-PN) and other peripheral neuropathies, including diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT).
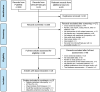
Methods: Literature searches identified studies reporting neuropathic progression, measured by Neuropathy Impairment Score (NIS) or NIS-Lower Limbs (NIS-LL). Our study also included unpublished data from a clinical registry of patients who were diagnosed with different peripheral neuropathies and seen at the Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) during 2016-2020. Meta-analysis and meta-regression models examined and compared annual progression rates, calculated from extracted data, between studies of ATTRv-PN and other peripheral neuropathies.
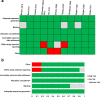
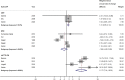
Results: Data were synthesized from 15 studies in which NIS and/or NIS-LL total scores were assessed at least twice, with ≥12 weeks between assessments, among untreated patients with ATTRv-PN or other peripheral neuropathies. Meta-analysis models yielded that the annual progression rate in NIS total scores was significantly different from zero for studies in ATTRv-PN and CMT (11.77 and 1.41; both P < 0.001), but not DPN (- 1.96; P = 0.147). Meta-regression models showed significantly faster annual progression in studies in ATTRv-PN, which statistically exceeded that in other peripheral neuropathies by 12.45 points/year for NIS, and 6.96 for NIS-LL (both P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Peripheral nervous function deteriorates more rapidly in patients with ATTRv-PN than for other peripheral neuropathies. These findings may improve understanding of the natural history of neuropathy in ATTRv-PN, facilitate early diagnosis, and guide the development of assessment tools and therapies specifically targeting neuropathic progression in this debilitating disease.
Keywords: Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy; Meta-analysis; Neuropathic progression; Neuropathy impairment score; Peripheral neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
XL, AY, NB, and JB are employees of QualityMetric, which received funding from Akcea Therapeutics for conducting this research. MVL and DB are employees of and own stock in Akcea Therapeutics. CK has received support from Acceleron, Akcea Therapeutics, Alexion, Alnylam, Biogen, Cytokinetics, CSL Behring, and Sanofi Genzyme. BV declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

