A randomized placebo-controlled phase I clinical trial to evaluate the immunomodulatory activities of Atractylodes lancea (Thunb) DC. in healthy Thai subjects
- PMID: 33579265
- PMCID: PMC7879636
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-020-03199-6
A randomized placebo-controlled phase I clinical trial to evaluate the immunomodulatory activities of Atractylodes lancea (Thunb) DC. in healthy Thai subjects
Abstract
Background: Atractylodes lancea (Thunb) DC. (AL) and bioactive compounds β-eudesmol and atractylodin have been demonstrated in the in vitro and in vivo studies for their potential clinical use in cholangiocarcinoma. The study was a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase I clinical trial to evaluate the immunomodulatory effect of AL in human subjects.
Methods: The modulatory effects of AL and β-eudesmol and atractylodin on TNFα and IL6 expression in PBMCs were measured using real-time PCR. Blood samples were collected from forty-eight healthy subjects following oral administration of a single or multiple dosing of capsule formulation of the standardized AL extract or placebo. Serum cytokine profiles, lymphocyte subpopulations (B lymphocytes, CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes, CD4+ T-helper lymphocytes, and NK cells), and cytotoxic activity of PBMCs against the cholangiocarcinoma cell line CL-6 were evaluated using cytometric bead array (CBA) with flow cytometry analysis.
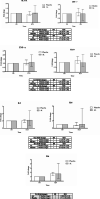
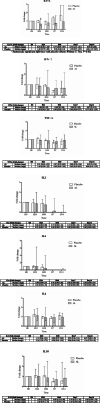
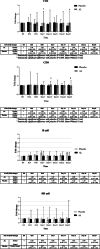
Results: AL extract at almost all concentrations significantly inhibited both TNFα and IL6 expression in Con A-mediated inflammation in PBMCs. β-Eudesmol at all concentrations significantly inhibited only IL6 expression. Atractylodin at the lowest concentration significantly inhibited the expression of both cytokines, while the highest concentration significantly inhibited only IL6 expression. The administration of AL at a single oral dose of 1000 mg appeared to decrease IFNγ and IL10 and increase B cell, while significantly increase NK and CD4+ and CD8+ cells. A trend of increasing (compared with placebo) in the cytotoxic activity of PBMCs at 24 h of dosing was observed. AL at multiple dosing of 1000 mg for 21 days tended to decrease the production of all cytokines, while significantly inhibited IL17A production at 24 h of dosing. In addition, a significant increase in CD4+ and CD8+ cells was observed. A trend of increase in the cytotoxic activity of PBMCs was observed at 24 h but terminated at 48 h of dosing.
Conclusions: The results confirm the immunomodulatory activity of AL in humans. This activity, in complementary with the direct action of AL on inducing cholangiocarcinoma cell apoptosis, suggests its potential role for CCA control.
Trial registration: Retrospectively registered on 17 October 2020 [Thai Clinical Trials Registry (TCTR: www.clinical trials.in.th ) Number TCTR20201020001 #].
Keywords: Atractylodes lancea; Atractylodin; Cholangiocarcinoma; Immunomodulatory activity; β-Eudesmol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Atractylodin and β-eudesmol from Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC. Inhibit Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Proliferation by Downregulating the Notch Signaling Pathway.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Feb 1;24(2):551-558. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.2.551. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 36853304 Free PMC article.
-
Growth inhibitory effect of β-eudesmol on cholangiocarcinoma cells and its potential suppressive effect on heme oxygenase-1 production, STAT1/3 activation, and NF-κB downregulation.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017 Nov;44(11):1145-1154. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12818. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28732110
-
Embryotoxicity evaluation of atractylodin and β-eudesmol using the zebrafish model.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021 Jan;239:108869. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2020.108869. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32805444
-
The Role of Herbal Medicine in Cholangiocarcinoma Control: A Systematic Review.Planta Med. 2023 Jan;89(1):3-18. doi: 10.1055/a-1676-9678. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Planta Med. 2023. PMID: 35468650
-
Therapeutic potential and pharmacological activities of β-eudesmol.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021 Apr;97(4):984-996. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13823. Epub 2021 Feb 7. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021. PMID: 33449412 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiproliferative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Deprungsith Formulation and Its Bioactive Compounds Against Mild Psoriasis and Potential of Metabolic Herb-Drug Interactions.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2023 Jan-Dec;28:2515690X231191101. doi: 10.1177/2515690X231191101. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 37553989 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 and Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio Indices Identify Patients with Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 11;12(4):844. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040844. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672199 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Microenvironment and its Implications for Antitumor Immunity in Cholangiocarcinoma: Future Perspectives for Novel Therapies.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Aug 21;18(14):5369-5390. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.73949. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36147461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of artesunate combined with Atractylodes lancea or Prabchompoothaweep remedy extracts as adjunctive therapy for the treatment of cerebral malaria.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Sep 20;23(1):332. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04150-1. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37730604 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical studies of toxicity and anti-cholangiocarcinoma activity of the standardized capsule formulation of Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Jun 7;23(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03992-z. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37287012 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

