Contraceptive dynamics during COVID-19 in sub-Saharan Africa: longitudinal evidence from Burkina Faso and Kenya
- PMID: 33579717
- PMCID: PMC7886665
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjsrh-2020-200944
Contraceptive dynamics during COVID-19 in sub-Saharan Africa: longitudinal evidence from Burkina Faso and Kenya
Abstract
Introduction: Evidence from health emergencies suggests COVID-19 will disrupt women's sexual and reproductive health (SRH). In sub-Saharan Africa, which experiences the highest rates of unintended pregnancy and unsafe abortion globally, COVID-19 is projected to slow recent progress toward universal access to contraceptive services.
Methods: We used longitudinal data collected from women at risk of unintended pregnancy in Burkina Faso (n=1186) and Kenya (n=2784) before (November 2019-February 2020) and during (May-July 2020) COVID-19 to quantify contraceptive dynamics during COVID-19; examine sociodemographic factors and COVID-19 experiences related to contraceptive dynamics; and assess COVID-19-related reasons for contraceptive non-use. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regressions were used to examine correlates of contraceptive dynamics amid COVID-19.
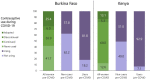
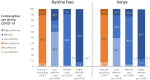
Results: Most women did not change their contraceptive status during COVID-19 (68.6% in Burkina Faso and 81.6% in Kenya) and those who did were more likely to adopt a method (25.4% and 13.1%, respectively) than to discontinue (6.0% and 5.3%, respectively). Most women who switched contraceptives were using methods as or more effective than their pre-pandemic contraception. Economic instability related to COVID-19 was associated with increased contraceptive protection in Burkina Faso but not in Kenya. Altogether, 14.4% of non-contraceptive users in Kenya and 3.8% in Burkina Faso identified COVID-19-related reasons for non-use.
Conclusions: The vast majority of women at risk of unintended pregnancy did not change their contraceptive status during COVID-19, and more women adopted than discontinued methods. A minority of women reported COVID-19-related reasons for non-use, underscoring the importance of expanding safe modes of service delivery during health crises.
Keywords: COVID-19; contraception behavior; epidemiology; family planning services; reproductive health services; surveys and questionnaires.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Coronavirus Resource Center . Johns Hopkins University, 2020. Available: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/region [Accessed 21 Sep 2020].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical