CMTM6 and PD-L1 coexpression is associated with an active immune microenvironment and a favorable prognosis in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 33579737
- PMCID: PMC7883863
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001638
CMTM6 and PD-L1 coexpression is associated with an active immune microenvironment and a favorable prognosis in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain-containing 6 (CMTM6), a programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) regulator, is widely expressed in various tumors and regulates the immune microenvironment. However, its prognostic value remains controversial, and the roles of CMTM6 in colorectal cancer (CRC) are still unknown. In this study, we aimed to elaborate the expression patterns of CMTM6 and PD-L1 in CRC and investigate their relationship with the infiltration of T cells and the prognosis of patients with CRC.
Methods: Analysis of CMTM6 mRNA levels, gene ontology enrichment analysis and single-sample gene set enrichment analysis were performed in a The Cancer Genome Atlas colon cancer cohort. The expression of CMTM6 and PD-L1 and the infiltration of T cells in tumor tissues from our cohort containing 156 patients with CRC receiving adjuvant chemotherapy and 77 patients with CRC without chemotherapy were examined by immunohistochemistry assay.
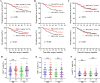
Results: CMTM6 expression was upregulated in CRC compared with normal colon tissues, and CMTM6 levels were lower in advanced tumors than in early-stage tumors. High expression of CMTM6 correlated with lower pT stage and more CD4+/CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and predicted a favorable prognosis in CRC. PD-L1 was expressed in CRC tissues at a low level, and PD-L1 positivity in tumor stroma (PD-L1(TS)), but not PD-L1 positivity in cancer cells (PD-L1(CC)), was associated with an increased density of CD4+ TILs and a favorable prognosis. The coexpression status of CMTM6 and PD-L1(TS) divided patients with CRC into three groups with low, moderate and high risks of progression and death, and patients with CMTM6High/PD-L1(TS)+ status had the longest survival. Moreover, the prognostic value of CMTM6/PD-L1 expression was more significant in patients with CRC treated with adjuvant chemotherapy than in those not treated with chemotherapy.
Conclusion: CMTM6 has a critical impact on the immune microenvironment and can be used as an independent prognostic factor for CRC. The coexpression status of CMTM6 and PD-L1 can be used as a new classification to stratify the risk of progression and death for patients with CRC, especially for patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. These findings may provide insights into improving responses to immunotherapy-included comprehensive treatment for CRC in the future.
Keywords: B7-H1 antigen; biomarkers; gastrointestinal neoplasms; immunohistochemistry; lymphocytes; tumor; tumor-infiltrating.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: No, there are no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
