Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonist PET Tracer Development: Assessment in Nonhuman Primates
- PMID: 33579806
- PMCID: PMC8882897
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.120.256008
Dopamine D1 Receptor Agonist PET Tracer Development: Assessment in Nonhuman Primates
Abstract
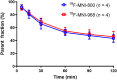
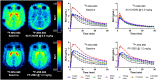
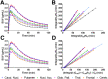
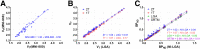
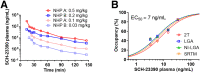
Non-catechol-based high-affinity selective dopamine D1 receptor (D1R) agonists were recently described, and candidate PET ligands were selected on the basis of favorable properties. The objective of this study was to characterize in vivo in nonhuman primates 2 novel D1R agonist PET radiotracers, racemic 18F-MNI-800 and its more active atropisomeric (-)-enantiomer, 18F-MNI-968. Methods: Ten brain PET experiments were conducted with 18F-MNI-800 on 2 adult rhesus macaques and 2 adult cynomolgus macaques, and 8 brain PET experiments were conducted with 18F-MNI-968 on 2 adult rhesus macaques and 2 adult cynomolgus macaques. PET data were analyzed with both plasma-input-based methods and reference-region-based methods. Whole-body PET images were acquired with 18F-MNI-800 from 2 adult rhesus macaques for radiation dosimetry estimates. Results:18F-MNI-800 and 18F-MNI-968 exhibited regional uptake consistent with D1R distribution. Specificity and selectivity were demonstrated by dose-dependent blocking with the D1 antagonist SCH-23390. 18F-MNI-968 showed a 30% higher specific signal than 18F-MNI-800, with a nondisplaceable binding potential of approximately 0.3 in the cortex and approximately 1.1 in the striatum. Dosimetry radiation exposure was favorable, with an effective dose of about 0.023 mSv/MBq. Conclusion:18F-MNI-968 has significant potential as a D1R agonist PET radiotracer, and further characterization in human subjects is warranted.
Keywords: D1 receptor; PET imaging; Parkinson disease; agonist; schizophrenia.
© 2021 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures

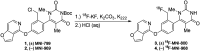
References
-
- Hall H, Sedvall G, Magnusson O, Kopp J, Halldin C, Farde L. Distribution of D1- and D2-dopamine receptors, and dopamine and its metabolites in the human brain. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1994;11:245–256. - PubMed
-
- Meador-Woodruff JH, Damask SP, Wang J, Haroutunian V, Davis KL, Watson SJ. Dopamine receptor mRNA expression in human striatum and neocortex. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1996;15:17–29. - PubMed
-
- Schneider JS, Sun ZQ, Roeltgen DP. Effects of dihydrexidine, a full dopamine D-1 receptor agonist, on delayed response performance in chronic low dose MPTP-treated monkeys. Brain Res. 1994;663:140–144. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
