Cholesterol as a modulator of cannabinoid receptor CB2 signaling
- PMID: 33580091
- PMCID: PMC7881127
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-83245-6
Cholesterol as a modulator of cannabinoid receptor CB2 signaling
Abstract
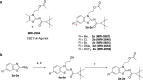
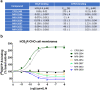
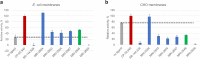
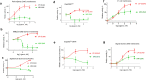
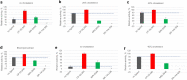
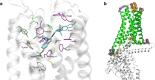
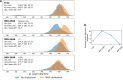
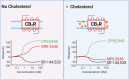
Signaling through integral membrane G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) is influenced by lipid composition of cell membranes. By using novel high affinity ligands of human cannabinoid receptor CB2, we demonstrate that cholesterol increases basal activation levels of the receptor and alters the pharmacological categorization of these ligands. Our results revealed that (2-(6-chloro-2-((2,2,3,3-tetramethylcyclopropane-1-carbonyl)imino)benzo[d]thiazol-3(2H)-yl)ethyl acetate ligand (MRI-2646) acts as a partial agonist of CB2 in membranes devoid of cholesterol and as a neutral antagonist or a partial inverse agonist in cholesterol-containing membranes. The differential effects of a specific ligand on activation of CB2 in different types of membranes may have implications for screening of drug candidates in a search of modulators of GPCR activity. MD simulation suggests that cholesterol exerts an allosteric effect on the intracellular regions of the receptor that interact with the G-protein complex thereby altering the recruitment of G protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Allosteric and orthosteric pharmacology of cannabidiol and cannabidiol-dimethylheptyl at the type 1 and type 2 cannabinoid receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 May;176(10):1455-1469. doi: 10.1111/bph.14440. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29981240 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological data of cannabidiol- and cannabigerol-type phytocannabinoids acting on cannabinoid CB1, CB2 and CB1/CB2 heteromer receptors.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:104940. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104940. Epub 2020 May 26. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32470563
-
Negative allosteric modulators of cannabinoid receptor 2: protein modeling, binding site identification and molecular dynamics simulations in the presence of an orthosteric agonist.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020 Jan;38(1):32-47. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2019.1567384. Epub 2019 Feb 5. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020. PMID: 30652534 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric modulators targeting cannabinoid cb1 and cb2 receptors: implications for drug discovery.Future Med Chem. 2019 Aug;11(15):2019-2037. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2019-0005. Future Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31517528 Review.
-
Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptor ligand specificity and the development of CB2-selective agonists.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(14):1428-43. doi: 10.2174/092986708784567716. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18537620 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual mechanisms of cholesterol-GPCR interactions that depend on membrane phospholipid composition.Structure. 2023 Jul 6;31(7):836-847.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2023.05.001. Epub 2023 May 25. Structure. 2023. PMID: 37236187 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid regulation of the glucagon receptor family.J Endocrinol. 2024 May 6;261(3):e230335. doi: 10.1530/JOE-23-0335. Print 2024 Jun 1. J Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38614123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Goods and Bads of the Endocannabinoid System as a Therapeutic Target: Lessons Learned after 30 Years.Pharmacol Rev. 2023 Sep;75(5):885-958. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.122.000600. Epub 2023 May 10. Pharmacol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37164640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane protein Bcsdr2 mediates biofilm integrity, hyphal growth and virulence of Botrytis cinerea.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 28;108(1):398. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13238-8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38940906 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian Nonparametric Analysis of Residence Times for Protein-Lipid Interactions in Molecular Dynamics Simulations.J Chem Theory Comput. 2025 Apr 22;21(8):4203-4220. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.4c01522. Epub 2025 Apr 2. J Chem Theory Comput. 2025. PMID: 40172093
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

