The LaserFIB: new application opportunities combining a high-performance FIB-SEM with femtosecond laser processing in an integrated second chamber
- PMID: 33580462
- PMCID: PMC7818346
- DOI: 10.1186/s42649-020-00044-5
The LaserFIB: new application opportunities combining a high-performance FIB-SEM with femtosecond laser processing in an integrated second chamber
Abstract
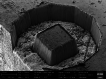
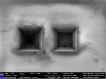
The development of the femtosecond laser (fs laser) with its ability to provide extremely rapid athermal ablation of materials has initiated a renaissance in materials science. Sample milling rates for the fs laser are orders of magnitude greater than that of traditional focused ion beam (FIB) sources currently used. In combination with minimal surface post-processing requirements, this technology is proving to be a game changer for materials research. The development of a femtosecond laser attached to a focused ion beam scanning electron microscope (LaserFIB) enables numerous new capabilities, including access to deeply buried structures as well as the production of extremely large trenches, cross sections, pillars and TEM H-bars, all while preserving microstructure and avoiding or reducing FIB polishing. Several high impact applications are now possible due to this technology in the fields of crystallography, electronics, mechanical engineering, battery research and materials sample preparation. This review article summarizes the current opportunities for this new technology focusing on the materials science megatrends of engineering materials, energy materials and electronics.
Keywords: Crossbeam laser; Dual chamber SEM; FIB-SEM; Femtosecond laser; LaserFIB; PFIB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests other than as the manufacturer of the LaserFIB system. This review provides an objective view of the new, unique technology.
Figures






References
-
- Ali AM, Ong A, Konneh M. Micromilling of tungsten carbide using focused ion beam. 2005.
-
- Barnett R, Mueller S, Hiller S, Pérez-Willard F, Strickland J, Dong H. Rapid production of pillar structures on the surface of single crystal CMSX-4 superalloy by femtosecond laser machining. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020;127:105941. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2019.105941. - DOI
-
- Boyd S, Dornfeld D, Krishnan N, Moalem M. Environmental challenges for 45-nm and 32-nm node CMOS logic. 2007.
-
- T.L.R.K. Burnett, Large volume serial section tomography by Xe Plasma FIB dual beam microscopy. Ultramicroscopy, 119–129 (2016) 10.1016/j.ultramic.2015.11.001 - PubMed
-
- Daemi SR, Tan C, Volkenandt T, Cooper SJ, Palacios-Padros A, Cookson J, et al. Visualizing the carbon binder phase of battery electrodes in three dimensions. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018;1(8):3702–3710. doi: 10.1021/acsaem.8b00501. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
