Magnetization-prepared GRASP MRI for rapid 3D T1 mapping and fat/water-separated T1 mapping
- PMID: 33580909
- PMCID: PMC8197608
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.28679
Magnetization-prepared GRASP MRI for rapid 3D T1 mapping and fat/water-separated T1 mapping
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to (i) develop Magnetization-Prepared Golden-angle RAdial Sparse Parallel (MP-GRASP) MRI using a stack-of-stars trajectory for rapid free-breathing T1 mapping and (ii) extend MP-GRASP to multi-echo acquisition (MP-Dixon-GRASP) for fat/water-separated (water-specific) T1 mapping.
Methods: An adiabatic non-selective 180° inversion-recovery pulse was added to a gradient-echo-based golden-angle stack-of-stars sequence for magnetization-prepared 3D single-echo or 3D multi-echo acquisition. In combination with subspace-based GRASP-Pro reconstruction, the sequence allows for standard T1 mapping (MP-GRASP) or fat/water-separated T1 mapping (MP-Dixon-GRASP), respectively. The accuracy of T1 mapping using MP-GRASP was evaluated in a phantom and volunteers (brain and liver) against clinically accepted reference methods. The repeatability of T1 estimation was also assessed in the phantom and volunteers. The performance of MP-Dixon-GRASP for water-specific T1 mapping was evaluated in a fat/water phantom and volunteers (brain and liver).
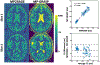
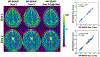
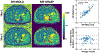
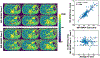
Results: ROI-based mean T1 values are correlated between the references and MP-GRASP in the phantom (R2 = 1.0), brain (R2 = 0.96), and liver (R2 = 0.73). MP-GRASP achieved good repeatability of T1 estimation in the phantom (R2 = 1.0), brain (R2 = 0.99), and liver (R2 = 0.82). Water-specific T1 is different from in-phase and out-of-phase composite T1 (composite T1 when fat and water signal are mixed in phase or out of phase) both in the phantom and volunteers.
Conclusion: This work demonstrated the initial performance of MP-GRASP and MP-Dixon-GRASP MRI for rapid 3D T1 mapping and 3D fat/water-separated T1 mapping in the brain (without motion) and in the liver (during free breathing). With fat/water-separated T1 estimation, MP-Dixon-GRASP could be potentially useful for imaging patients with fatty-liver diseases.
Keywords: MP-Dixon-GRASP; MP-GRASP; T1 mapping; fat/water separation; free-breathing; golden-angle radial.
© 2021 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Li Feng and Kai Tobias Block are named co-inventors of a patent (Patent number 9921285) on the GRASP imaging technique. Kai Tobias Block and Thomas Benkert are employees of Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Germany.
Figures





References
-
- Block KT, Uecker M, Frahm J. Undersampled radial MRI with multiple coils. Iterative image reconstruction using a total variation constraint. Magn Reson Med. 2007;57:1086–1098. - PubMed
-
- Glover GH, Pauly JM. Projection reconstruction techniques for reduction of motion effects in MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1992;28:275–289. - PubMed
-
- Block KT, Chandarana H, Milla S, et al. Towards routine clinical use of radial stack-of-stars 3D gradient-echo sequences for reducing motion sensitivity. J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med. 2014;18:87.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

