Synergistic efficacy of combined EGFR and HDAC inhibitors overcomes tolerance to EGFR monotherapy in salivary mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- PMID: 33581505
- PMCID: PMC8026571
- DOI: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.105166
Synergistic efficacy of combined EGFR and HDAC inhibitors overcomes tolerance to EGFR monotherapy in salivary mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Abstract
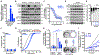
Objectives: Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) is the most common type of salivary gland malignancy. Advanced or high-grade MECs are refractory to chemotherapy, often leading to tumor recurrence/metastasis and abysmal ~35% 5-year survival. Causal links have been established between Epithelial Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) activation and poor outcome. Herein we investigated the therapeutic efficacy of EGFR inhibition against MEC using in vitro pre-clinical models.
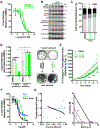
Materials and methods: Five human MEC cell lines were used in cell viability, cytotoxicity, apoptosis, cell cycle, 2D-clonogenicity, and 3D-spheroid formation assays following treatment with Erlotinib (EGFR inhibitor), SAHA (Histone Deacetylase inhibitor; HDAC) and CUDC-101 (dual EGFR-HDAC inhibitor). Effects on MEC cancer stem cells were evaluated using flow cytometry. Gene expression and pathway regulation were evaluated via qPCR and Western blot, respectively.
Results: MEC cells enter a quiescent, non-proliferative yet rapidly reversible drug tolerant state upon EGFR inhibition. Despite robust suppression of MEC cell proliferation, no discernable apoptosis is detected. Combination of EGFR and HDAC inhibitors exhibits synergistic effects, exerting ~5-fold more potent cell cytotoxicity compared to HDAC or EGFR monotherapy. CUDC-101, a single molecule with dual EGFR-HDAC inhibitor moieties, exerts irreversible and potent cytotoxic activity against MEC cells and blunts MEC cancer stem-cell tumorigenicity.
Conclusion: MEC cells are intrinsically tolerant to EGFR inhibition. Combining EGFR and HDAC inhibitors exerts synergistic and potent cytotoxic effects, suggesting that EGFR inhibitors still hold significant promise against MEC. Future studies are needed to assess the applicability and efficacy of dual EGFR-HDAC inhibitors for the clinical management of MEC.
Keywords: CUDC-101; Drug synergy; Drug tolerance; EGFR; HDAC; Head and neck cancer; Mucoepidermoid carcinoma; Salivary cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
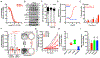
Similar articles
-
The CRTC1-MAML2 fusion is the major oncogenic driver in mucoepidermoid carcinoma.JCI Insight. 2021 Apr 8;6(7):e139497. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.139497. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 33830080 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Notch and EGFR signaling in human mucoepidermoid carcinoma.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jan 21;6(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00388-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33473104 Free PMC article.
-
Apicidin inhibits cell growth by downregulating IGF-1R in salivary mucoepidermoid carcinoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2015 Apr;33(4):1899-907. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3776. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25647264
-
Molecular heterogeneity in mucoepidermoid carcinoma: conceptual and practical implications.Head Neck Pathol. 2013 Mar;7(1):23-7. doi: 10.1007/s12105-013-0432-5. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Head Neck Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23459841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expanding the cytological and architectural spectrum of mucoepidermoid carcinoma: The key to solving diagnostic problems in morphological variants.Semin Diagn Pathol. 2024 Jul;41(4):182-189. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2024.04.001. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38609754 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Therapeutics Targeting Upstream Regulators and Interactors of EHMT1/2.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 9;14(12):2855. doi: 10.3390/cancers14122855. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell culture in salivary gland tumor research: molecular insights of pathogenic targets and personalized medicine.Cytotechnology. 2025 Apr;77(2):70. doi: 10.1007/s10616-025-00726-6. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Cytotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40028370 Review.
-
Role of Histone Deacetylases in the Pathogenesis of Salivary Gland Tumors and Therapeutic Targeting Options.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 12;24(12):10038. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210038. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDACs/mTOR inhibitor synergizes with pyrotinib in HER2-positive pancreatic cancer through degradation of mutant P53.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Dec 1;22(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02807-4. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36457011 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted intervention of tumor microenvironment with HDAC inhibitors and their combination therapy strategies.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Feb 4;30(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02326-8. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39905506 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- El-Naggar AKCJ, Grandis JR, Takata TSP. WHO Classification of Head and Neck Tumours. 4th Editio. IARC Press; 2016.
-
- Jacob PK, McCoy JM. Diagnostic Imaging of Salivary Gland Pathology. 2nd Edition ed.-Chapter 2. Wiley-Blackwell; 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

