Dysfunctions in Infants' Statistical Learning are Related to Parental Autistic Traits
- PMID: 33582879
- PMCID: PMC8531064
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-021-04894-0
Dysfunctions in Infants' Statistical Learning are Related to Parental Autistic Traits
Abstract
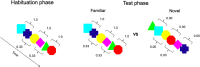
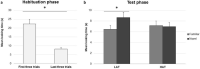
Statistical learning refers to the ability to extract the statistical relations embedded in a sequence, and it plays a crucial role in the development of communicative and social skills that are impacted in the Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Here, we investigated the relationship between infants' SL ability and autistic traits in their parents. Using a visual habituation task, we tested infant offspring of adults (non-diagnosed) who show high (HAT infants) versus low (LAT infants) autistic traits. Results demonstrated that LAT infants learned the statistical structure embedded in a visual sequence, while HAT infants failed. Moreover, infants' SL ability was related to autistic traits in their parents, further suggesting that early dysfunctions in SL might contribute to variabilities in ASD symptoms.
Keywords: Autistic traits; Early marker; Infants; Visual statistical learning.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®) Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Pub; 2013.
-
- Aslin RN, Saffran JR, Newport EL. Computation of conditional probability statistics by 8-month-old infants. Psychological Science. 1998;9(4):321–324. doi: 10.1111/1467-9280.00063. - DOI
-
- Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S, Skinner R, Martin J, Clubley E. The autism-spectrum quotient (AQ): Evidence from asperger syndrome/high-functioning autism, males and females, scientists and mathematicians. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 2001;31(1):5–17. doi: 10.1023/A:1005653411471. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bayley N. Bayley scales of infant and toddler development. New York: Pearson; 2006.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

