Muscle activity and acute stress in fibromyalgia
- PMID: 33583408
- PMCID: PMC7883576
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-021-04013-1
Muscle activity and acute stress in fibromyalgia
Abstract
Background: Fibromyalgia (FM) patients are likely to differ from healthy controls in muscle activity and in reactivity to experimental stress.
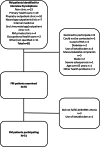
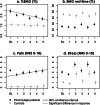
Methods: We compared psychophysiological reactivity to cognitive stress between 51 female FM patients aged 18 to 65 years and 31 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. They underwent a 20-minute protocol consisting of three phases of relaxation and two phases of cognitive stress. We recorded surface electromyography normalized to maximum voluntary muscle contraction (%EMG), the percentage of time with no muscle activity (EMG rest time), and subjective pain and stress intensities. We compared group reactivity using linear modelling and adjusted for psychological and life-style factors.
Results: The FM patients had a significantly higher mean %EMG (2.2 % vs. 1.0 %, p < 0.001), pain intensity (3.6 vs. 0.2, p < 0.001), and perceived stress (3.5 vs. 1.4, p < 0.001) and lower mean EMG rest time (26.7 % vs. 47.2 %, p < 0.001). In the FM patients, compared with controls, the pain intensity increased more during the second stress phase (0.71, p = 0.028), and the %EMG decreased more during the final relaxation phase (-0.29, p = 0.036). Within the FM patients, higher BMI predicted higher %EMG but lower stress. Leisure time physical activity predicted lower %EMG and stress and higher EMG rest time. Higher perceived stress predicted lower EMG rest time, and higher trait anxiety predicted higher pain and stress overall.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that repeated cognitive stress increases pain intensity in FM patients. FM patients also had higher resting muscle activity, but their muscle activity did not increase with pain. Management of stress and anxiety might help control FM flare-ups.
Trial registration: Retrospectively registered on ClinicalTrials.gov ( NCT03300635 ).
Conflict of interest statement
Eija Kalso has served on the advisory boards of Orion Pharma and Pfizer. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Trapezius activity of fibromyalgia patients is enhanced in stressful situations, but is similar to healthy controls in a quiet naturalistic setting: a case-control study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013 Mar 18;14:97. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-14-97. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013. PMID: 23506457 Free PMC article.
-
Heart rate variability responses to cognitive stress in fibromyalgia are characterised by inadequate autonomous system stress responses: a clinical trial.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 13;13(1):700. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27581-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36639565 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuated adrenergic responses to exercise in women with fibromyalgia--a controlled study.Eur J Pain. 2008 Apr;12(3):351-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2007.07.007. Epub 2007 Sep 10. Eur J Pain. 2008. PMID: 17827042
-
Abnormal muscle membrane function in fibromyalgia patients and its relationship to the number of tender points.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012 Nov-Dec;30(6 Suppl 74):44-50. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 23191983
-
Acute effects of physical exercise on the serum insulin-like growth factor system in women with fibromyalgia.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Jan 25;18(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1402-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 28122522 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Elevated highly sensitive C-reactive protein in fibromyalgia associates with symptom severity.Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2022 Jun 25;6(2):rkac053. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkac053. eCollection 2022. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2022. PMID: 35832286 Free PMC article.
-
Pain-sensorimotor interactions: New perspectives and a new model.Neurobiol Pain. 2024 Jan 20;15:100150. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2024.100150. eCollection 2024 Jan-Jun. Neurobiol Pain. 2024. PMID: 38327725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic utility of deep tendon reflex responses in rectus femoris and triceps brachii in fibromyalgia: a clinical and electrophysiological study.Rheumatol Int. 2025 Feb 21;45(3):57. doi: 10.1007/s00296-025-05808-4. Rheumatol Int. 2025. PMID: 39982496 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac output and arteriovenous oxygen difference contribute to lower peak oxygen uptake in patients with fibromyalgia.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Jul 1;24(1):541. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06589-2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 37393269 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation modulates masseter muscle activity, pain perception, and anxiety levels in university students: a double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial.Front Integr Neurosci. 2024 Jul 10;18:1422312. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2024.1422312. eCollection 2024. Front Integr Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39051059 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

