Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura Complicated by Hepatitis C Virus-related Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis after Rituximab Therapy
- PMID: 33583904
- PMCID: PMC8381184
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.6758-20
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura Complicated by Hepatitis C Virus-related Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis after Rituximab Therapy
Abstract
We herein report the case of a 54-year-old Japanese man with hepatitis C virus (HCV)-related membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN), which developed at the time of relapse of immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) after rituximab therapy. Antiviral therapy for HCV led to the improvement of both MPGN and ITP. Rituximab therapy may have contributed to the exacerbation of HCV infection and induced the development of HCV-related MPGN and the relapse of ITP. Our case suggested that HCV treatment should be prioritized over rituximab therapy for HCV-positive patients with ITP and that antiviral therapy for HCV may be effective for treating ITP itself.
Keywords: hepatitis C virus; immune thrombocytopenia; membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis; rituximab.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
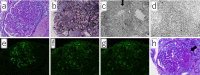
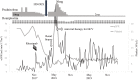
Similar articles
-
Refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis successfully treated with rituximab: a case associated with hepatitis C virus infection.Hong Kong Med J. 2009 Jun;15(3):201-8. Hong Kong Med J. 2009. PMID: 19494376
-
Rapidly deteriorating renal function with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis Type 1 associated with hepatitis C treated successfully with steroids and antiviral therapy: a case report and review of literature.Clin Nephrol. 2008 Apr;69(4):298-301. doi: 10.5414/cnp69298. Clin Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18397706 Review.
-
Rituximab treatment for immune-complex-mediated membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis.Immunotherapy. 2018 Sep;10(12):1027-1031. doi: 10.2217/imt-2018-0031. Immunotherapy. 2018. PMID: 30185139
-
Hepatitis C virus-related proteins in kidney tissue from hepatitis C virus-infected patients with cryoglobulinemic membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis.Hepatology. 1997 May;25(5):1237-44. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250529. Hepatology. 1997. PMID: 9141444
-
Treatment of hepatitis C-virus-related glomerulonephritis.Kidney Int. 2006 Feb;69(3):436-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000142. Kidney Int. 2006. PMID: 16514428 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune-Complex Mediated Mesangial Proliferative Glomerulonephritis with Full-House Pattern Observed During Treatment of Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura.Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2024 Dec 24;17:11795476241307123. doi: 10.1177/11795476241307123. eCollection 2024. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39735784 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological considerations in pharmacotherapy of rheumatology patients with liver disease: a brief narrative review.Reumatologia. 2024;62(4):282-293. doi: 10.5114/reum/191791. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Reumatologia. 2024. PMID: 39381733 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cines DB, Blanchette VS. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 346: 995-1008, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Cooper N, Bussel J. The pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopaenic purpura. Br J Haematol 133: 364-374, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Kashiwagi H. Reference guide for management of adult idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP): 2019 version. Rinsho Ketsueki 60: 877-896, 2019. - PubMed
-
- Miyakawa Y, Katsutani S, Yano T, et al. . Efficacy and safety of rituximab in Japanese patients with relapsed chronic immune thrombocytopenia refractory to conventional therapy. Int J Hematol 102: 654-661, 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

